The EU’s adoption of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) impacts organizations operating in the financial sector and third-party companies that provide ICT (information and communication technology). While organizations have until 2024 to comply with DORA, it’s crucial to start taking steps to protect your organization from harmful and costly data breaches.
The question is—are you ready for compliance?
The urgency of implementing DORA is demonstrated by the increase in online transactions across sectors and the cyber threats that target them. The recent hack of MOVEit, a transfer file management program, is a prime example. Initially an attack on an American software company, it has since compromised the data of 600 organizations globally—affecting almost 40 million people. The massive data breach has impacted financial organizations, pharmacies, educational organizations, motor vehicle authorities, government contractors, and more.
DORA’s regulatory framework helps mitigate and prevent these types of cyber threats by ensuring that organizations can withstand, respond to, and recover from threats and ICT-related disruptions. Improving your operational resilience can’t be put off until the compliance date; your data is worth protecting now. This post will provide essential twelve steps to DORA Act compliance to help you start protecting your organization and prepare you for full enactment of these new regulations.
What is the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA), and when does compliance begin?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is an EU financial regulation that requires organizations to be able to protect, detect, contain, recover, and repair their ICT capabilities in the case of cyberattacks or ICT-related disruptions.
Before the adoption of DORA, EU financial regulations focused on financial organizations and allowed them to manage operational risks by allocating capital. Financial organizations were not tasked with managing the many components of operational resilience, exposing many vulnerabilities to be taken advantage of by cybercriminals.
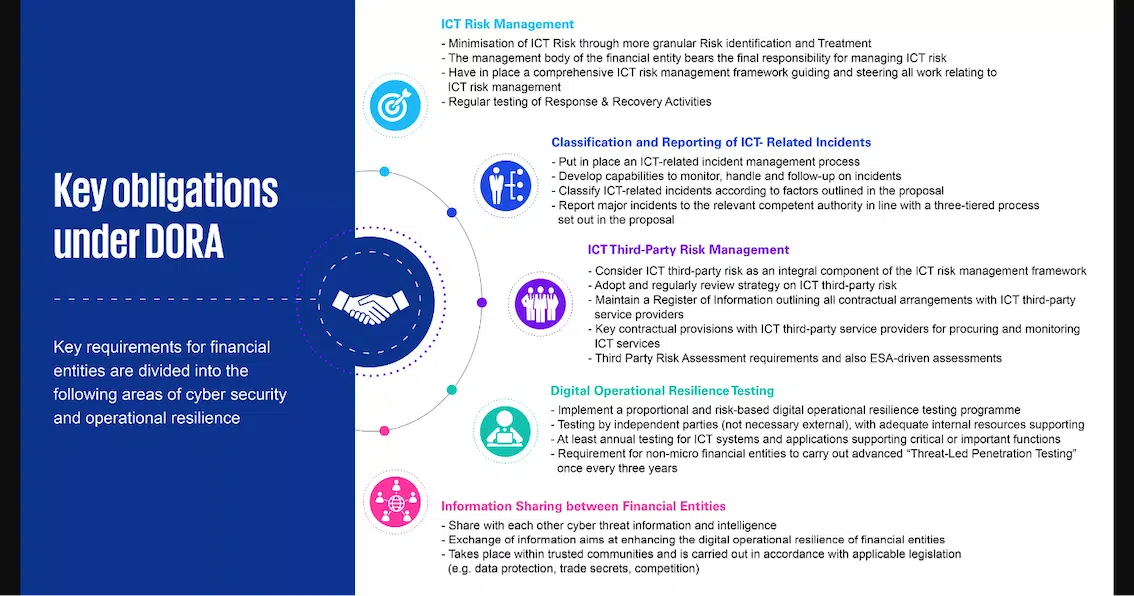
DORA goes beyond previous regulations and requires financial institutions and other impacted organizations to manage every component of operational resilience. The new regulatory framework includes details for third-party risk monitoring, set rules for ICT risk management, incident reporting, and operational resilience testing.
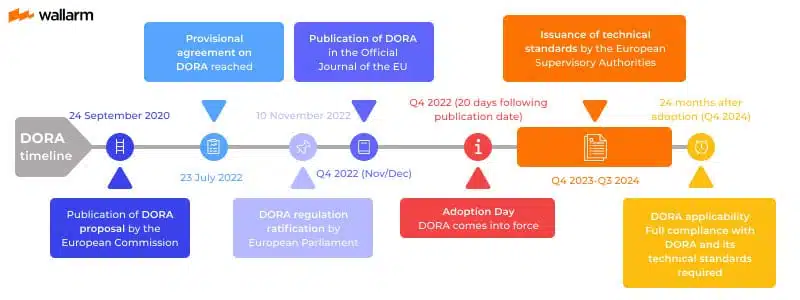
A two-year implementation period began in January 2023, and compliance with DORA will be applicable in all EU member states as of January 17, 2024.
Why is DORA compliance critical for the finance sector?
DORA’s regulations are enforceable in all EU Member States and apply to more than just financial institutions. Financial entities, including banks, investment firms, insurance companies, and crypto-asset service providers, are all subject to DORA compliance. It extends beyond previous regulations confined to financial institutions by including critical third parties offering IT and cybersecurity services to financial companies.
From 2021 to 2022, data breach costs caused by third-party breaches increased from $4.33 million to $4.55 million. DORA’s framework closes gaps that allow such breaches to happen.
While implementing DORA requires additional work to meet compliance requirements, there are benefits for your organization. By improving your operational resilience, you protect sensitive data for your organization and clients. Additionally, as more organizations adopt DORA requirements, the entire market is protected from cyber threats and costly data breaches. It is also expected to reduce the overall costs of compliance and cut through bureaucracy by standardizing regulations for all EU Member States.
Financial entities that are not DORA-compliant can be subject to a variety of penalties to be determined by the laws of each EU member country, including:
- Public reprimands
- Withdrawal of authorization
- Remedial measures
- Compensation for damages
- Criminal charges
- Administrative fines
12 Essential Steps to Become Compliant with the DORA Act
Navigating new regulation compliance requirements can be overwhelming. To help you make sense of it all, we’ve broken down DORA compliance into twelve steps:
1. Know the Requirements for Your Organization
To become DORA compliant, you must first know what the requirements and obligations mean for your organization. Familiarize yourself with the regulation to thoroughly understand what’s required for your organization to build an effective cyber resilience framework. Specialized training may be a good option, such as programs like the DORA Certified Compliance Specialist (DCCS).
2. Run a Risk Assessment of Your Organization
A risk assessment of your entire organization and its extended supply chain will give you a better understanding of which parts are vulnerable to cyber threats. Use automated solutions to help identify and assess any possible risks.
3. Consult with Multiple Teams
Use the collective knowledge of multiple teams to analyze risk assessment results and contribute to building a compliance strategy. The compliance process includes IT security, compliance, legal, risk management, management, and external counterparties, so it is crucial to work with all relevant teams to get a comprehensive view of the cyber risks to your organization—and then collaborate to build an effective strategy.
4. Conduct Employee Training
DORA compliance requires training all employees in digital operational resilience. Board and C-level executives are responsible for an organization’s operational resilience, making them vital for successfully integrating DORA requirements. This requires the appropriate training based on the level of complexity of the functions each employee is responsible for. CybeReady’s training programs can educate your employees on the importance of cybersecurity and how to protect your organization from cyber threats.

5. Build an Operational Resilience Strategy
To achieve DORA compliance, your organization must have a cyber resilience strategy that meets the requirements outlined in Article 6(8). A business continuity plan should provide a detailed plan for how your organization will respond to cyber threats, data breaches, and other operational disruptions.
6. Consider Third-party Service Vendors
DORA’s framework includes regulations for third-party service providers, so they must be considered in your risk assessments and while building your operational resilience strategy. Examine the importance, complexity, and scale of ICT services and your organization’s reliance on them. By factoring in all of their vectors, you can build an effective risk management strategy to ensure your organization meets DORA’s requirements.
7. Perform Regular DORT and Pen Testing
DORA compliance requires regular penetration testing every three years. Pen tests and Digital Operational Resilience Testing (DORT) are testing approaches that can help you become DORA-compliant by allowing you to identify and mitigate risks through mimicking real-life threats.
8. Automate Threat Detection
To maintain DORA compliance, you must have proper detection capabilities to alert you of any incidents, anomalies, or cyber-attacks. This requires installing automated threat-detection solutions, which must have sufficient resources and capabilities allocated to them per Article 10 of DORA.

9. Regularly Review and Update Your Resilience Strategy
Conducting operational resilience tests can provide helpful information and prepare you for DORA compliance and mandatory reviews. Review DORT results and data from previous attacks. This will allow you to make informed decisions and adjustments to improve the effectiveness of your operational resilience strategy over time.
10. Prepare for the Worst-case Scenario
A key to maintaining long-term DORA compliance is preparing for the worst-case scenario. You need to prioritize your remediation actions by identifying vulnerabilities, then rank solutions based on factors such as the likelihood of occurrence and impact on your organization.
11. Secure Your Data
Ensure you have the technical and organizational measures required to protect customer data properly. Follow all data protection regulations that apply to EU Member States, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
12. Be Prepared to Provide Evidence of Compliance
You will need to prove compliance with the DORA Act by regularly testing, assessing, and simulating possible threats. Providing evidence of resilience tests demonstrates to regulators that your organization is committed to the continued safety and security of data. CybeReady’s Compliance Tool can help with instantly generated compliance reports, so you are always ready for a potential audit or statement of proof.
Get Your Organization Ready for DORA Compliance with CybeReady
The integration period for the DORA Act has started, and with that comes many changes for financial institutions and other impacted organizations. DORA compliance will bring more security and stability to the financial system, while non-compliance could result in costly penalties. If you’re worried about your organization’s preparedness for DORA compliance, CybeReady can help improve your digital operational resilience.
Successful security training for every employee safeguards your organization and is critical for DORA compliance. With CybeReady, financial organizations can ensure effective employee training so they have the necessary knowledge to recognize and report cyber threats against the organization.
Schedule a demo today to discover how our training can strengthen your organization’s security resilience and prepare you for DORA compliance.












