Thousands of financial institutions across Europe are embracing change and going digital. While this change may be convenient for customers, convenience comes at a cost, and the growing danger of digital threats now puts the financial industry at risk.
Data breaches cause severe operational damage and can result in catastrophic financial costs. In 2022, the global average data breach cost was a staggering 4.35 million U.S. dollars across all industries and 5.97 million U.S. dollars per breach in the global financial sector.
As cyber threats continue to escalate, protecting sensitive customer data is more challenging than ever. In response to these growing challenges facing the digital financial industry, the EU recently passed the DORA Compliance act to enhance data protection and privacy and minimize cyber-attacks for financial organizations operating in the EU.
In this article, we look at what DORA is and who it affects and provide actionable steps for ensuring compliance. Keep reading to stay ahead of the curve and safeguard your organization’s future.
Building Digital Resilience: Understanding DORA
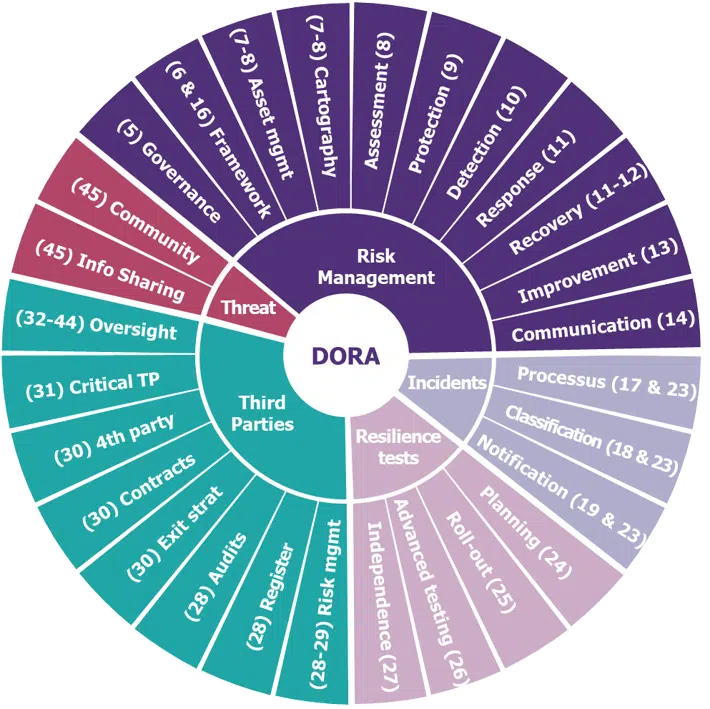
DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) is a regulatory framework created by the European Council to address the need for operational resilience in the financial sector during events that significantly affect operational functionality, particularly cyber attacks. The act sets a series of requirements for the security of network and information systems of organizations operating in the financial sector and third parties providing ICT (information and communication technology) related services. The aim is to ensure that all firms build the cyber resilience required to withstand, respond to, and recover from all types of ICT-related disruptions and threats to prevent and mitigate cyber threats.
Guarding the Financial Ecosystem: Who’s Affected by DORA and How?
DORA affects financial entities, including banks, insurance companies, investment firms, crypto-asset service providers, and critical third parties offering financial companies IT and cybersecurity services. DORA is a regulation, making it enforceable and directly applicable in all EU Member States. The act supplements the Network and Information Security (NIS2) directive and addresses possible overlaps via a “lex specialis” exemption. Compliance with DORA’s requirements is also a significant step towards protecting the privacy of sensitive personal data, such as financial records, mandated by GDPR.
Time to Take Action: When DORA Is Set to Come into Force
The regulation entered into force on January 17, 2023, and will apply from January 17, 2024. Each EU member state will transpose the “required” aspects of the regulation into national legislation. The relevant European Supervisory Authorities will develop technical standards that all financial services institutions adhere to. The relevant national competent authorities will supervise compliance with the regulation and enforce it where appropriate. By the 17th of January 2026, the European Commission will evaluate whether there is a need for increased obligations on statutory auditors and audit firms concerning digital operational resilience.
Enhance Your DORA Compliance in 20 Steps
Becoming DORA compliant requires a comprehensive approach to operational resilience that ensures firms fulfill all the security obligations outlined in the act. While this may seem overwhelming, below we outline 20 steps that can help you remain DORA compliant at all times:
1. Understand the requirement and all your obligations
The first step towards becoming DORA compliant is understanding its requirements and obligations. You’ll need to begin by becoming familiar with the regulation. You may even consider specialized training, such as the DORA Certified Compliance Specialist (DCCS) program. By completing this training, individuals can gain in-depth knowledge of the regulation.
2. Assess the cyber risks that threaten your organization
Understanding the cyber risks that exist across your extended supply chain is crucial. Leveraging automated solutions (see step 16) can aid in identifying and assessing these risks. This way, you can spot potential vulnerabilities and proactively mitigate them.

3. Develop a digital operational resilience strategy
Another step towards maintaining DORA compliance is to ensure your ICT risk management framework includes a digital operational resilience strategy that covers key elements outlined in Article 6(8) of the DORA requirements. You can also monitor and improve the strategy’s effectiveness over time by analyzing incidents and learning from mandatory reviews and operational resilience tests.
4. Utilize the assistance of multiple teams
It’s essential that multiple teams, such as IT security, legal, compliance, and risk management, as well as management and external counterparties, are involved in the compliance process. This way, you can get a comprehensive view of your organization’s cyber risks and take a holistic approach to compliance.
5. Consider the regulations when using third-party service providers
When dealing with contractual agreements with ICT third-party service providers, consider the scale, complexity, and importance of ICT-related dependencies and risks. Doing so enables informed decisions on risk management and ensures that your organization meets the regulation’s requirements.
6. Empower your organization’s leadership
DORA holds the Board and C-level executives responsible for a firm’s operational resilience, so senior management should lead in implementing DORA’s requirements. To enable this, leadership should receive appropriate training and ensure high-level security professionals, such as a CCRO (Certified Cyber Risk Officer), are available to understand the subject matter, make informed decisions, and take responsibility for their implications on the organization.
7. Create a company culture that prioritizes security
While empowering leadership is important, every member of the organization is responsible for maintaining and ensuring DORA compliance. Creating a security-focused company culture can help with DORA compliance by ensuring that the entire staff is invested in maintaining the company’s security and that security is considered in all aspects of the business.
8. Prioritize your remediation actions
Maintaining compliance in the long term requires preparing for the worst-case scenario. You can do this by identifying vulnerabilities in your organization (see step 2) and prioritizing your remediation actions based on potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This ensures that proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect your operations can be implemented as soon as possible in order of priority to minimize the operational impact of a potential breach.
9. Be prepared to provide evidence of compliance
Be prepared to demonstrate compliance with DORA regulations by regularly assessing, testing, and simulating potential risks. Producing evidence of resilience shows regulators your commitment to safety and stability. Another way you can provide evidence of your activities is by drafting your strategies in compliance with DORA’s response obligations. You will also need to determine the competent authority to report to and when to contact them.
10. Monitor external sources for potential risks
Stay informed of potential risks by monitoring external sources of information, such as industry reports and threat intelligence feeds. Financial institutions should share intelligence on threats, respecting confidentiality, GDPR, and competition guidelines, to help protect both themselves and other institutions from falling victim to those threats in the future. Modalities and participation conditions must be defined, and relevant authorities notified. You can incorporate this information into your resilience strategy for proactive risk mitigation.
11. Identify your critical functions
Identify the functions essential to the company’s operations in line with DORA regulation requirements. This will be a focal point for the company’s efforts to enhance its resilience and clarify which functions should be a high priority for security.

12. Encourage Secure Development Practices
Promoting secure coding practices is essential for DORA compliance. Tools like penetration testing (see step 15) can identify potential weaknesses in systems and applications, while employee training can help create a security-aware culture. CybeReady’s training program includes a security awareness program, phishing simulations program, audit/compliance tool, and elastic security program that can also help develop a security-first mindset across the organization and implement security-focused development practices.
13. Implement streamlined incident reporting
Expand the scope of incident reporting and streamline the process to meet DORA’s requirements. Rapid investigation and response to incidents should also be encouraged to mitigate the impact of a breach. Breach reports can also be used to help detect unknown intrusions in other networks.
14. Analyze incidents to improve your strategy
Prior incidents can influence future strategy. Incorporating lessons learned from major incidents, difficulties activating business continuity plans, surveillance of cyber threats, and operational resilience tests can enhance your DORA compliance strategy. A yearly report should be made to the management body with findings and recommendations. This will help organizations stay compliant with DORA’s regulations and ensure operational resilience.
15. Conduct regular penetration testing
Regular penetration testing is crucial for DORA compliance. Competent authorities determine entities subject to advanced security testing based on impact factors, financial stability, and ICT risk profiles. Threat-based penetration testing (TLPT) mimics real-life threats and tests critical production systems of financial entities every 3 years, using the TIBER-EU framework. External testers must demonstrate expertise in threat intelligence and adhere to ethical frameworks with no conflict of interest and approval from relevant authorities. By identifying areas that require further attention, organizations can prioritize remediation efforts.
16. Automate your threat detection
To remain DORA compliant, it’s important to have proper detection capabilities for anomalies, incidents, and cyber attacks. This means installing EDRs, XDRs, scanners, SIEMs, and other threat-detection solutions. According to Article 10 of DORA, financial entities must allocate sufficient resources and capabilities for this purpose. To meet the requirements of the regulation, the detection mechanisms must enable multiple layers of control, define alert thresholds and criteria, and initiate incident response processes.
17. Empower your employees with employee training

To comply with DORA, employee training is mandatory for digital operational resilience. This training must be applicable to all employees and senior management staff, with a level of complexity based on their functions. CybeReady’s training program can help transform your organization’s security culture and educate employees on the importance of cybersecurity. By avoiding potential risks, you can protect your organization from cyber threats.
The CISO, in conjunction with Human Resources and division managers, can guide the choice of training courses or providers. Implementing employee training is a crucial step that should be taken as soon as possible. Tools such as CybeReady’s training program can help make training smoother, faster, and more engaging, allowing you to transform your security culture and help your employees understand the importance of cybersecurity. By empowering your employees with the knowledge to identify and avoid potential risks, you create an extra level of security, protecting your organization from cyber threats.
18. Create an ICT Risk Management Framework
DORA mandates comprehensive testing to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities to financial entities’ operations, detailed in Chapter 4. Digital operational resilience testing is crucial for preparedness and identifying weaknesses and includes periodic testing of the ICT risk management framework and threat-led penetration testing. Basic ICT testing is required for all entities, with advanced testing only for those deemed significant by competent authorities.
19. Review and understand digital operational resilience testing
Digital Operational Resilience Testing (DORT) is a proactive testing approach that helps organizations identify and mitigate potential disruptions to their digital systems and services. It simulates real-world scenarios to assess an organization’s ability to maintain essential services in the face of disruptions, helping financial institutions maintain compliance with DORA. In the European Union, DORT is essential for improving operational resilience and complying with regulatory frameworks like DORA.
20. Regularly review and update your resilience strategies
To ensure compliance with DORA regulation requirements and preparedness for potential disruptions, it is essential to regularly review and update your digital operational resilience strategy and policy on ICT Third Parties (TPs). Regulations are constantly shifting and being updated, new developments are made in the cybersecurity sphere, and new cyber attacks gain popularity with attackers. In such a dynamic cyber environment, it’s essential to remain ahead of the curve by regularly reviewing and updating your strategies and new developments in the cybersecurity industry. This practice will help your organization stay aligned with the regulations and maintain a proactive approach toward operational resilience.
Strengthening Your Institution’s Resilience: Key Takeaways from DORA Regulations
Secure and resilient IT systems are essential to ensure the financial sector’s stability. DORA regulations are designed to ensure that financial entities have effective risk management frameworks and controls in place to prevent, respond to, and recover from ICT incidents. While fulfilling all the obligations included in the act can be challenging, as a financial entity, it is crucial to comply with the DORA regulations to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Maintaining a high level of security requires participation from all employees, and that is where employee education comes in. Financial institutions can significantly reduce the likelihood of cyber incidents by educating employees on the importance of proactive security measures and empowering them to identify and report potential security risks.
Investing in employee training is not only critical for compliance with DORA, but it is also a necessary step toward building a strong and resilient security culture. By providing engaging and effective training, financial entities can ensure their employees have the knowledge and skills to safeguard the organization against cyber threats.
But keeping regular employee training fresh, engaging, and topically relevant can be challenging, which is why CybeReady offers an employee training platform designed to help financial institutions meet their compliance obligations and improve their security posture. Schedule a demo today to learn how our innovative platform can empower your employees and strengthen your organization’s security resilience.












