Imagine this scenario: You receive a seemingly innocent text message on your phone telling you to click on a link to claim a special offer. Without suspecting foul play, you comply, only to find out later that you’ve fallen victim to a smishing attack. Smishing (a combination of “SMS” and “phishing”) refers to the act of using text messages to deceive individuals and manipulate them into sharing sensitive information or performing harmful actions.
As mobile communication continues to be an integral part of our daily lives, incidents of smishing attacks continue to increase. Smishing attacks surged by nearly 700% in the first half of 2021 and have persistently escalated since, prompting the US government to issue an official warning in 2022, urging citizens to remain vigilant.
With the increasing rise of smishing attacks, it’s crucial for professionals in all industries, especially finance, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing, to understand the risks and take proactive measures to prevent such attacks. This post will dive deep into smishing, explore its various forms, examine its risks and consequences, and provide essential steps to prevent yourself and your organization from falling victim to smishing attacks.
Why You Should Care About Smishing
Smishing attacks use similar tactics to phishing attacks but target users through a different attack vector. Unlike phishing, which primarily targets email or website users, smishing takes a more personal approach, targeting users directly through their mobile devices.
Smishing poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. It takes advantage of the widespread use of mobile phones and text messaging to exploit human vulnerability and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Similarly to phishing, attackers using smishing techniques often impersonate trusted entities or use social engineering tactics to manipulate victims into divulging personal information, installing malware, or clicking on malicious links.
Both individuals and organizations are at risk, and anyone can be a target, as smishing attacks aim to exploit our trust in communication channels and trick us into divulging personal information or downloading malware.
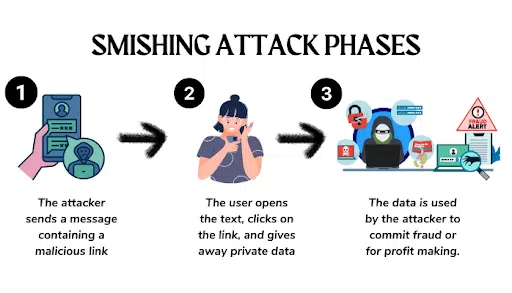
What are the different kinds of smishing attacks?
Smishing attacks come in various forms, each with specific strategies and objectives. These include:
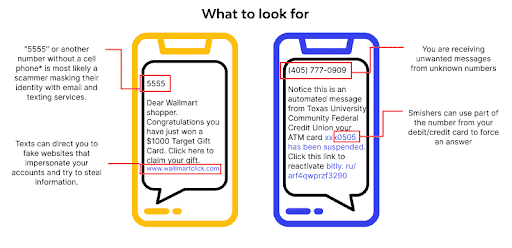
Malicious Link Messages
These messages typically contain a shortened URL that, when clicked, directs the recipient to a fake website designed to steal personal information or deliver malware.
Prize or Lottery Scams
Fraudsters send text messages claiming that the recipient has won a prize or lottery, urging them to respond with personal information or pay a fee to claim the prize.
Financial Scams
Attackers impersonate financial institutions, sending messages that appear legitimate and requesting sensitive banking details or login credentials.
Urgent or Emergency Messages
These messages exploit people’s emotions and create a sense of urgency, urging recipients to take immediate action, such as making a payment or revealing personal information.
Impersonation of Government Agencies
Attackers may masquerade as government agencies or law enforcement entities, sending text messages that appear official and demanding immediate action or personal information. This type of attack was especially prevalent in both phishing and smishing scams throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Risks and Consequences of Smishing Attacks
The risks associated with smishing attacks are multifaceted and can have far-reaching consequences. Here are some of the primary risks you need to be aware of:
- Financial Loss – Falling victim to a smishing attack can result in unauthorized access to your bank accounts, credit card fraud, or even funds being siphoned off without your knowledge.
- Identity Theft – By tricking individuals into revealing personal information such as dates of birth, passwords, or Social Security numbers, smishing attacks enable cybercriminals to steal identities and perpetrate other fraudulent activities.
- Malware Infections – Clicking on malicious links sent via smishing messages can install malware on your device, compromising your personal data and potentially providing unauthorized access to cyber criminals.
- Reputation Damage – If personal or sensitive information is leaked in a smishing attack, it can tarnish your personal and professional reputation and potentially impact your relationships with others.
- Data Breaches – Smishing attacks can lead to data breaches, where sensitive information of individuals or organizations is exposed, leading to potential legal and financial consequences.
- Compromised Security – Falling victim to smishing attacks can undermine the overall security posture of individuals and organizations, making them more susceptible to future cyber threats.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance Issues – Failing to adequately protect sensitive information from smishing attacks can result in non-compliance with data protection regulations, such as Europe’s GDPR or California’s CCPA, leading to legal repercussions and financial penalties.
6 Steps to Prevent Smishing Attacks
1. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Implementing 2FA for all your online accounts adds an extra level of security that goes beyond passwords. By requiring a second form of verification via a unique code sent to your cellular phone or mobile device, 2FA helps prevent unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.
2. Be Wary of Unsolicited Messages
Exercise caution when interacting with text messages from unknown sources or those offering unexpected prizes, discounts, or urgent requests. These could be smishing attacks attempting to deceive you into sharing information or downloading harmful content.
3. Be Skeptical of Text Messages
Even when it may seem like you know the sender, exercise caution when receiving text messages, particularly those that request personal information or urge immediate action. Verify the sender’s identity before responding or clicking on any links. Legitimate organizations will typically not request sensitive information via text message.

4. Don’t Share Sensitive Information
Never share sensitive data via SMS, such as account numbers, social security numbers, or passwords. Remember, reputable organizations will never ask you to provide such information through this channel.
5. Install Security Software
Keep your mobile device protected by installing reputable antivirus and security software. Regularly update these applications to ensure you have the latest protection against emerging threats.
6. Educate Yourself and Your Employees
Invest in comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training to educate yourself and your employees about smishing attacks, their risks, and prevention strategies. Educational programs used to raise awareness of phishing attacks can also educate employees against smishing attacks, which use similar tactics. Programs like CybeReady’s phishing simulation training can provide valuable insights and empower individuals to identify and respond effectively to smishing attempts.
Strengthening Your Defenses Against Smishing
Smishing attacks continue to increase, targeting individuals and organizations across various industries. By understanding the nature of smishing attacks, their risks, and their consequences, we can proactively protect ourselves and our organizations.
Employing measures like enabling 2FA, being skeptical of text messages, and investing in cybersecurity awareness training can significantly enhance our defenses against smishing attacks. These measures strengthen our ability to identify and thwart smishing attempts and create a culture of cybersecurity awareness within our organizations.
As an industry leader in cybersecurity training, CybeReady offers comprehensive solutions to bolster your organization’s security posture. Our phishing simulation training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to effectively identify and thwart phishing, smishing, and other fraud-reliant cyber-attacks.
Take action by requesting a demo today to fortify your defenses and stay one step ahead of cyber threats.











