Picture this: A thriving SaaS company is diligently working to expand its digital presence and empower its remote workforce. But behind the hustle and bustle, there’s a lurking danger—hackers are finding and using gaps in their old security system, putting sensitive data and smooth operations at risk. These flaws were more than a weak spot; they hinted at major future disruptions and a significant blow to their market reputation. But what could their InfoSec team do?
In this scenario, adopting Zero Trust Security isn’t just a choice; it’s a necessity. It’s the shield that safeguards your organization from sophisticated attacks, both external and internal—and aligns seamlessly with the evolving landscape of regulations and data privacy. A recent report showed that 80% of respondents globally have already adopted it or will do so soon.
This in-depth guide to Zero Trust will explain what it is, why you need it, how it works, and how you can synergize it with cybersecurity education to bolster your organization’s cyber defenses.
What is Zero Trust Security?
With remote workforces becoming the norm, an even broader attack surface can be exploited by cyber threats. The traditional security model relies on perimeter-based defenses and operates on trust once users are inside the network. However, over the years, studies have indicated that most organizations have experienced insider data breaches—and Zero Trust Security addresses this issue head-on.
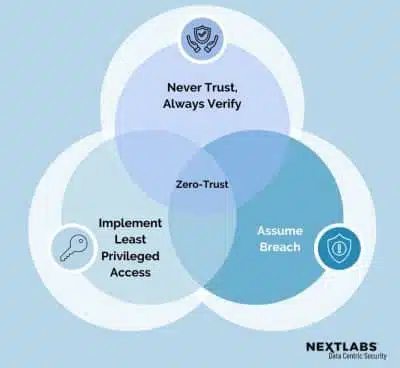
Often referred to as Zero Trust, it is not just a cybersecurity framework; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach security. At its foundation, Zero Trust is the concept of “never trust, always verify.”
This security model ensures no entity, whether inside or outside your network perimeter, is trusted by default. Regardless of location, every user, device, and application is rigorously authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before being granted access to resources.
How does Zero Trust Security work?
Zero Trust Security operates on the premise that threats exist outside and inside the network. It encompasses a set of guiding principles and architecture that apply to any environment, including your organization’s.
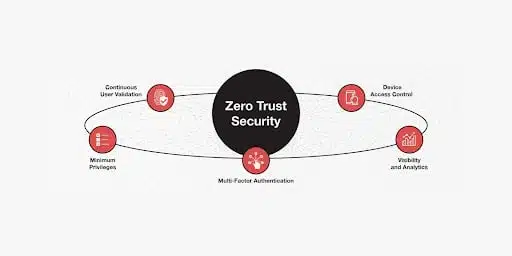
The key components of Zero Trust are:
- Micro-Segmentation – This involves breaking down your network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting lateral movement for attackers.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) – Strictly control and monitor who has access to what, ensuring users have the least privilege necessary.
- Continuous Monitoring – Continuously analyze traffic, user behavior, and device posture to identify anomalies and potential threats.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Enforce MFA to ensure that unauthorized access is thwarted even if a password is compromised.
- Encryption – Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive information.
- Policy Enforcement – Implement policies and controls that specify how data flows and who has access to it.
- Visibility and Analytics – This allows you to gain deep visibility into your network to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
The Benefits of Zero Trust
Embracing Zero Trust Security brings with it a variety of benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security – Zero Trust treats every user and device as untrusted, reducing the potential entry points for cyberattacks and minimizing the risk of breaches.
- Data Protection – Strict access controls and encryption safeguard critical data from unauthorized access.
- Improved Compliance – Zero Trust aligns seamlessly with regulatory data protection requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA, ensuring your organization remains on the right side of the law.
- Reduced Insider Threats – Continuous monitoring swiftly identifies and mitigates insider threats.
- Adaptability – Zero Trust can be implemented across various environments, making it a smart choice for a wide range of industries.
- Proactive Threat Detection – Constant network activity monitoring allows early threat detection.
- Enhanced Remote Work Security – Zero Trust offers robust security measures for data accessed from diverse locations and devices.
It’s a concept that’s gained traction globally and is utilized by many of the world’s leading tech corporations to improve cybersecurity and cyber resilience.
The 7 Pillars of Zero Trust
At the heart of Zero Trust Security lie the seven pillars that define its architecture:
1. Securing the Workforce
Workforce security revolves around the effective use of security tools, such as access control policies and authentication. These tools are crucial in verifying and validating users seeking network access before applying access policies. This step helps minimize the potential attack surface.
2. Ensuring Device Security
Device security, much like workforce security, places significant emphasis on identifying and authorizing devices attempting to connect to enterprise resources. These devices can range from user-controlled devices to fully autonomous ones, like IoT devices.
3. Safeguarding Workload Integrity
Workload security protects applications, digital processes, and public and private IT resources used for organizational operations. Each workload is fortified with security measures to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, or tampering with critical applications and services.
4. Securing Network Pathways
Within the context of the zero-trust model, network security assumes a pivotal role in micro-segmentation and the isolation of sensitive resources, thereby preventing unauthorized access by individuals or entities.
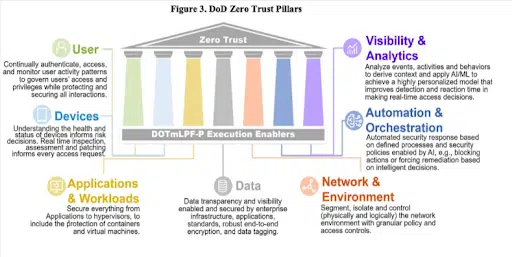
5. Zero-Trust Data Protection
The pillar of zero-trust data security focuses on carefully categorizing corporate data. Once appropriately categorized, data can be restricted to authorized personnel only. Additionally, this pillar involves determining the optimal data storage locations and implementing encryption mechanisms to protect data both in transit and at rest.
6. Enhancing Visibility and Leveraging Analytics
Comprehensive monitoring is vital for all security processes related to access control, segmentation, encryption, and data organization. The visibility and analytics aspect may recommend using AI for automating specific functions, including anomaly detection, configuration control, and data monitoring.
7. Streamlining Automation and Orchestration
The final pillar of the zero-trust framework addresses modern approaches to automate and centrally manage the entire zero-trust model, spanning LANs, WANs, wireless WANs, and public or private data centers.
Synergizing Zero Trust and Cybersecurity Education
Your organization’s workforce is the key to maximizing Zero Trust Security. Combining robust training with Zero Trust guidelines forms a strong line of defense since employees are often the first to spot cyber threats. This is why equipping them with the right skills is vital—and where CybeReady comes into play.
CybeReady provides top cybersecurity awareness training programs, helping employees quickly identify and handle potential threats. Using modern tools like phishing simulations and custom training courses, they ensure teams are ready to face a constantly changing threat landscape. This approach doesn’t just beef up a company’s defenses—it also builds a security awareness culture that makes your team the company’s most potent protection against growing insider threats.
Get in touch for a free demo to see how CybeReady’s training can elevate the effectiveness of your Zero Trust Security strategy.












