Vulnerability management has gained traction and importance in light of multiple high-profile cyber attacks. A staggering 14 ransomware attacks per second occurred in 2022, 20% more than a 2018 prediction, while the Cyber Threat Alliance found that the number of ransomware attacks increased by 365% in 2021, with an average payout of $1.1 million for victims.
Many cite the expansion of the attack surface as the reason why attacks continue to grow. Organizations can reduce the risk of a successful cyber attack by identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities and protecting their sensitive information, equipment, and assets.
Vulnerability management has become a key component in cybersecurity risk and compliance management. Organizations must allocate resources to this discipline to reduce cyber risk and avoid putting their clients and company at risk.
What is Vulnerability Management as a Service?
Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) is a cybersecurity service offered to corporate companies and public institutions by third-party providers. It is designed to help organizations identify, evaluate, and mitigate security vulnerabilities in their systems and infrastructure.
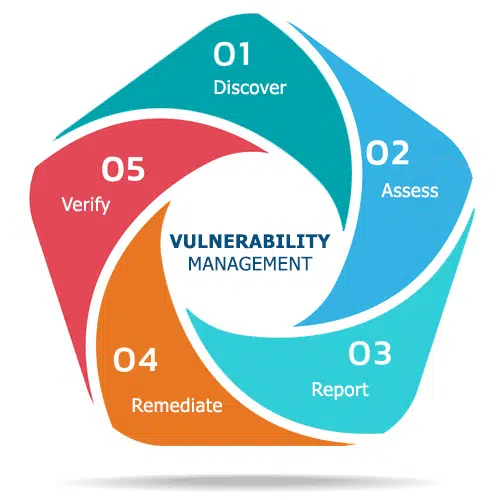
VMaaS typically includes the following components:
- Vulnerability Scanning: The use of automated tools to identify vulnerabilities in systems and infrastructure, including software, hardware, and network vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Assessment: The process of evaluating the potential impact of identified vulnerabilities and determining the risk they pose to an organization.
- Vulnerability Remediation: The process of mitigating or eliminating identified vulnerabilities through the implementation of security controls and patches.
- Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reports and analytics on vulnerabilities and the actions taken to remediate them.
VMaaS providers typically offer these services on a subscription basis and can be customized to meet an organization’s specific requirements. VMaaS benefits organizations that need more resources, expertise, or time to manage their vulnerability management programs or simply want to outsource this element of cybersecurity to experts.
VMaaS providers typically offer ongoing support so that organizations can stay updated with the latest vulnerabilities and best practices in vulnerability management. This allows organizations to focus on their core business operations while ensuring that their systems and infrastructure are secure.
What are the differences between a vulnerability, risk, and threat?
- A vulnerability: a weakness in a system or network that could be exploited by a threat.
- A threat: a potential danger that could exploit a vulnerability to cause harm to an asset.
- A risk: the potential harm that could occur.
The 4 main vulnerabilities
1. Network vulnerabilities
A computer network cybersecurity vulnerability refers to a weakness in the design, implementation, or configuration of a computer network that can make it more vulnerable to attack.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts files on a computer or a network and then demands a ransom in exchange for a decryption key.
- Phishing and social engineering attacks: These can trick users into divulging sensitive information after clicking on malicious links.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: This attack floods a network with traffic to disrupt access to resources.
- SQL injection: Where the attacker takes advantage of the vulnerability in the SQL database management system to gain unauthorized access to company systems.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: Where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties to steal sensitive information.
2. Operating system vulnerabilities
Operating system vulnerabilities include weaknesses in the design, implementation, or configuration of an operating system that can make it more vulnerable to attack.
- Unpatched software: If a patch for a vulnerability is available but not applied, the system will still be vulnerable.
- Weak or easily guessable passwords: Many operating systems have weak default passwords or enable users to choose easily guessable passwords, making them vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- Unnecessary services or open ports: Many operating systems come with services or open ports that are not required for regular operation, and these can be exploited if not correctly secured.
- Misconfigured permissions: Incorrectly configured file and directory permissions can provide unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Privilege escalation vulnerabilities: Some vulnerabilities enable attackers to gain elevated privileges on a system, which can then be used to access sensitive data or launch further attacks.
3. Configuration vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity configuration vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses or misconfigurations in the way a system or network is set up that can make it more vulnerable to attack.
- Inadequate access controls: Systems and networks that do not have robust access controls can enable unauthorized users to access sensitive data or launch attacks.
- Inadequate network segmentation: Poor network segmentation can enable an attacker who gains access to one part of the network to move laterally and access other parts of the network.
- Inadequate logging: Systems that do not log activity can make detecting and responding to security incidents difficult.
- Unpatched software: Systems that have unpatched software are vulnerable to known vulnerabilities.
- Inadequate backup and disaster recovery: Systems that do not have proper backup and disaster recovery plans can result in data loss or prolonged systems downtime.
4. Application vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity application vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in the design, implementation, or configuration of software applications that can make them more vulnerable to attack.
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): Vulnerabilities in the way an application handles user input can enable an attacker to inject malicious code into an application’s web page.
- Broken authentication and session management: Poor authentication and session management can enable an attacker to take over a user’s session or gain unauthorized access.
- Insecure communications: No using encryption or not correctly validating SSL/TLS certificates can enable an attacker to intercept or modify communications.
- Insecure storage: Not correctly encrypting sensitive data or protecting data at rest can enable an attacker to access or modify sensitive data.
- Insecure Cryptography: Vulnerabilities in the way an application handles encryption and decryption can enable an attacker to decrypt sensitive data and gain access to it.
What are vulnerability management tools?
There is an extensive range of cybersecurity vulnerability management tools on the market. Common vulnerability management tools include:
- Penetration testing tools: These tools simulate an attacker’s actions and try to exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access. Examples of penetration testing tools include Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Nmap.
- Configuration management tools: These tools manage and maintain the configuration of systems and network devices and can alert for misconfigurations. Examples of configuration management tools include Ansible, Chef, and Puppet.
- Asset management tools: These tools track network and system assets, including software and hardware. Examples of asset management tools include Device42, Lansweeper, and SolarWinds.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools: These tools collect and analyze log data from various sources, including network devices and systems, and can alert for security incidents. Examples of SIEM tools include Splunk, ArcSight, and LogRhythm.
- Endpoint protection platforms (EPP): These tools protect endpoint devices from malware and other cyber threats, typically through antivirus software and other security technologies. Examples include McAfee, Symantec, and Trend Micro.
5 reasons to consider Vulnerability Management as a Service
Vulnerability management should be high on the list of any CISO or security leader within an organization. Whether or not you outsource it as a service may depend on several factors.
These are the five top reasons why your company should consider a VMaaS provider:
1. Automation
VMaaS providers typically use automated tools and processes to scan for vulnerabilities regularly, which can help identify and address potential security issues more quickly and efficiently.
2. Scalability
Typically, with VMasS, it is possible to scale the services to meet the requirements of organizations of all sizes, making it a cost-effective option for businesses of any size.
3. Expertise
You will benefit from a team of security experts who can assist with interpreting scan results and recommending remediation steps, benefiting organizations that do not have in-house security expertise.
4. Compliance
VMaaS can help organizations meet compliance requirements by identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring they are addressed promptly.
5. Cost-effective
It eliminates the requirement for expensive hardware and software and the cost of hiring and training staff to manage it.
Limitations of Using Vulnerability Management Services
Despite the level of vulnerability management services deployed by an external company, more is needed to keep a company secure from vulnerabilities. Choosing a best-of-breed partner to fortify your own company’s cybersecurity can make a big difference when it comes to vulnerability management.
CybeReady provides a platform that enables organizations to evaluate and validate their cybersecurity defenses against simulated cyber attacks in a safe and controlled environment. The platform has features such as automated cyber attack simulations, detailed reporting, analytics, and a library of attack scenarios.