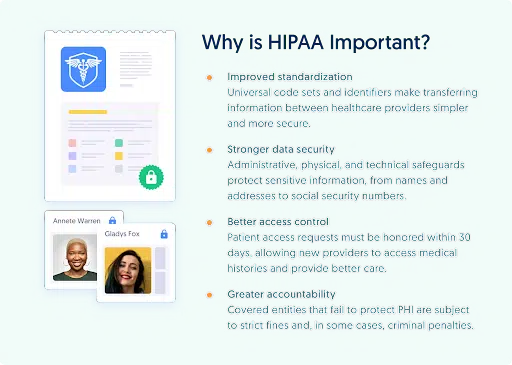
Healthcare information is a golden nugget for malicious actors. The black market pays a high price for confidential patient data, which can be used for extortion, identity theft, and even insurance fraud.
There were 284 U.S. healthcare data breaches in the first quarter of 2023, with over 19 million records breached in May alone. The reality is that there is a patient behind every statistic who deserves confidentiality and privacy. Without this right, patients lose trust in the healthcare system they rely on, so regulations like HIPAA are critical for patient care and data protection.
To better understand the importance of HIPAA compliance and its impact on safeguarding sensitive health information, let’s delve into what HIPAA entails and how it helps maintain patient data’s integrity and security.
What is HIPAA compliance?
HIPAA is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. It is a set of processes organizations in the healthcare industry must follow to prove that they take action to secure patient information (also called ‘protected health information’ or ‘PHI’).
The HIPAA compliance framework outlines what you must do to meet these regulations. The goal is to control access to sensitive patient data and ensure the healthcare industry and its employees maintain confidentiality and data privacy best practices.
What are the 3 rules of HIPAA?
1. The Privacy Rule
This rule shows you how to protect PHI and patient confidentiality by appointing a Privacy Officer, creating privacy notices, and giving patients the control to access their health information.
2. The Security Rule
The second Rule, Security, safeguards electronic PHI from unauthorized access, theft, and cyberattacks. It involves data security measures like encryption, data backup, and access control.
3. The Breach Notification Rule
This rule helps you get back on track in the event of a data breach when someone has gained unauthorized access to PHI. Under the Breach Notification Rule, you must inform all affected parties and take action to prevent data loss.
Who is HIPAA compliance applicable to?
HIPAA is relevant for any business in the healthcare industry, such as dentists, doctors, hospitals, health insurance providers, and research institutions.
HIPAA extends to:
- Covered entities: Any organization and person that works with patients and their data
- Business associates: Any third-party vendor or subcontractor that receives, creates, or transmits PHI data
- ePHI: Electronic patient data

What information is protected under HIPAA?
HIPAA protects everything classified as ‘health information,’ including electronic, written, and spoken data. It includes PHI that a healthcare provider has created, received, stored, or transmitted in the past, present, or future.
There’s no official list of PHI data because it’s difficult to define exactly what ‘health information’ is, but generally, HIPAA covers two types of information:
- Health information like test results or X-ray scans.
- Non-health information like phone numbers and gender that is stored in the same record set as health information. Non-health info that’s stored in a different record set is exempt.
What is a HIPAA compliance checklist, and why do you need one?
A HIPAA compliance checklist is a document outlining the clear steps your organization must take to meet the act’s requirements.
The checklist will help you:
- Get started with understanding HIPAA compliance.
- Ensure you remember all key areas.
- Conduct regular reviews in line with changing HIPAA regulations.
- Be aware of compliance regulations.
- Avoid penalties caused by human error or a lack of understanding.
- Improve patient trust.
Most importantly, using a HIPAA compliance checklist helps prevent a HIPAA violation.
Download your free HIPAA Compliance Checklist
What is a HIPAA violation?
HIPAA violations occur when you don’t meet the compliance standards. Common causes could be:
- Stolen hardware: The healthcare industry uses a lot of IoT devices and hardware, which can get stolen or misplaced.
- Human error: Misplacing files or using weak passwords can easily be overlooked if employees have yet to receive proper training.
- Access control failures: This happens if a bad actor gains access to PHI, highlighting the importance of authorization and validation.
- Failure to issue a breach notification: You must meet deadlines per the Breach Notification Rule to avoid getting hit with fines and losing patient trust.
If you fail to adhere to HIPAA, you could face fines of up to $50,000 for each violation, receive criminal penalties, or even lose your patients’ trust.
Here are three crucial things to know about HIPAA violations:
- Covered entities are legally obligated to comply with HIPAA regulations. Furthermore, business associates who handle PHI on behalf of covered entities are also subject to these regulations. Failure to comply can lead to violations.
- A breach that affects less than 500 individuals is considered ‘minor.’ You must notify the Department of Health and Human Services Office of Civil Rights (HHS OCR) by the end of the calendar year.
- A breach that affects over 500 individuals is considered ‘major.’ You must report it to the HSS, the media, and affected individuals within sixty days of knowing about it.
7 Steps to HIPAA Compliance
A HIPAA compliance checklist aims to ensure you understand which regulations apply to your business, what data is at risk, and what you should do to meet compliance obligations.
Follow these seven steps and use the free downloadable checklist to achieve HIPAA compliance:
1. Identify All Data
First, you can determine what data falls under HIPAA by identifying the PHI your business stores, transmits, creates, and receives. PHI doesn’t include all data your organization processes, so you must know what data must be protected under HIPAA, who has access to it, and how it is collected. Eighteen identifiers will help you determine which data is to be protected.

2. Understand the 3 Rules
Remember that there are three HIPAA Rules: Privacy, Security, and Data Breach Notification. Each requires different policies and safeguards, even though they’re closely related. By understanding the Rules, you can identify which ones apply to your organization and develop a compliance implementation and management plan.
3. Assign a HIPAA Officer and Delegate Accountability
Ideally, you should appoint someone in your organization with an IT background as the HIPAA Officer, whose job is to document and maintain security policies, like risk assessments and audits. Of course, they’ll need to be highly trained and even certified in HIPAA compliance to delegate accountability and take action if a violation occurs.
4. Perform a Risk Analysis and Assessment
Conducting a risk analysis helps you identify security vulnerabilities and areas where you fail to comply with HIPAA. You can see where your policies fall short and develop a plan to mitigate risk. Use the NIST HIPAA Security Toolkit Application to help you split your analysis between the three Rules and identify any training or new policies required to cover all bases.
5. Use IT Infrastructure Best Practices
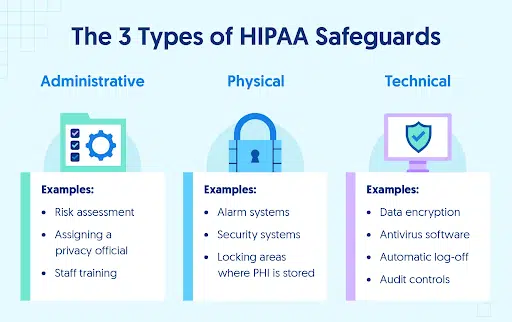
To meet the HIPAA Security Rule, you must ensure that PHI and ePHI are stored securely. There are a few ways to do this based on the type of data:
- Technical Data: Related to electronic PHI. Technical best practices include encryption, network security, and cloud security.
- Physical Data: Access control policies for physical equipment like computers, files, and servers
- Administrative Data: This includes the administrative tasks (like employee training and risk management) required for HIPAA.
6. Develop a Risk Management and Remediation Strategy
A risk management and remediation strategy is like a contingency plan in case you suffer a data breach or if someone violates HIPAA. It should outline what might happen and delegate tasks to the relevant employees. For example, you should submit a report to the Secretary of Health and Human Services within the deadline, conduct an internal investigation, and notify all affected parties.
7. Keep Documentation
You can only audit HIPAA compliance by keeping extensive documentation. Documenting everything (including policy changes and training sessions) helps you monitor your progress and shortcomings on the journey to meeting HIPAA regulations. Some audits will also require documentation; you’ll have to produce it if you suffer a breach, so it’s good to have it ready.
Does HIPAA compliance require employee training?
It’s best to communicate all HIPAA policies to every employee, which brings us to the eighth tip: implement employee HIPAA training.
The HIPAA Officer should be on hand to create internal resources and best practices, and answer any questions employees may have. You should document this training and include short top-up sessions in your organization’s calendar.
HIPAA is continuously changing, so it’s vital that your business stays up-to-date and feeds new information to all your employees. CybeReady’s training platform helps you meet and maintain HIPAA compliance requirements with engaging training modules that equip your employees with the skills they need to recognize, understand, and implement data privacy and security best practices.
For more information about how you can train your team to achieve HIPAA compliance, request a demo today.













