Almost every heist movie has a sequence where elaborate plans are created to get the plotters past the heavily guarded perimeter of their target facility. Then, once they’re inside, they drop their disguises and walk around like they own the place. For too many organizations, this is what happens when cybercriminals breach their network defenses.
As soon as infiltrators find a way to log in with valid credentials, the network grants them implicit trust—and they’re free to steal data, install malicious software, or sabotage critical systems. The only safe amount of trust you can grant by default is Zero Trust.
When you’re concentrating protective measures on the network perimeter and implicitly trusting any user who makes it through, it only takes a single compromised account or exploitable vulnerability to put all your data, devices, and applications at risk. The Zero Trust approach can make you twice as likely to avoid an outage and reduce the costs of a breach by up to $1.76 million, which is why 81% of cloud-based enterprises have started implementing zero trust data security principles.
Read on for an explanation of the key elements and benefits of Zero Trust Data Security (ZTDS), along with a guide to implementing it within your enterprise.
What are the principles of Zero Trust Data Security?
The core principle of Zero Trust Data Security (aka Zero Trust Data Protection) is that there can be no trust without verification. The default assumption should be that the network has already been breached, and security protocols must be designed around mitigating the impact. Any request to access or modify data must be explicitly verified with the full range of available user data, including their identity, device, location, and behavior.

When access is granted, it should always be on a least-privileged basis. Users are given rights only to perform the operations defined by their role or task, limited to the relevant timeframe and without granting any additional access privileges beyond what is absolutely necessary (for example, a user that only needs to read certain records should not be given the ability to edit or delete them). Activity logging and rule enforcement should be automated to the greatest extent possible.
What are the benefits of Zero Trust Data Security?
Zero Trust Data Security makes it harder for cybercriminals and other bad actors to do any real damage should they manage to hack into your network. Here are a few of the specific ways it strengthens your defenses, along with some additional benefits:
- Maximizes your data protection – By eliminating implicit trust and requiring individual verification for any data operations, a single breach is no longer sufficient to compromise everything on your network.
- Makes remote work safer – Remote work is now necessary for many organizations, expanding the potential attack surface. ZTDS mitigates this increased exposure by hardening internal defenses.
- Enhances your threat assessment capabilities – The continuous monitoring and analysis necessitated by ZTDS helps with the early detection of new vulnerabilities and suspicious activity.
- Improves policy enforcement – With a real-time view of access attempts across your network, you are better situated to develop and enforce effective security policies.
- Simplifies regulatory compliance – ZTDS architecture will help to bring your organization in line with the data protection regulations increasingly mandated by governments and industry associations.
What are the 3 stages of Zero Trust Data Security?
Implementation of Zero Trust Data Security occurs in three distinct stages:
- Data Resiliency: All data must be encrypted and backed up in order to facilitate protection and recovery efforts.
- Data Access: Role-based access controls and multifactor authentication are used to determine who can view and modify data.
- Detection and Analytics: The network is continuously monitored and analyzed to detect signs of a data breach, using advanced technology such as machine learning and predictive artificial intelligence.
Creating a Zero Trust Data Security Foundation in 3 Steps
Switching an entire organization over to a Zero Trust Data Security model can be a lengthy and involved process, but much of the essential groundwork can be laid during the initial phases of assessment, creating rules and policies, and providing training and education.
1. Assessment
One of the first things you need to do to pave the way for ZTDS is to assess your current data protection measures. You’ll want to identify the following:
- The types and locations of your current data stores
- Who needs access to your data, and for what purposes
- Which software programs are reading and writing data
- How data is accessed and transferred over your network
- The systems you have for monitoring your data
- The likely risk factors for your organization.
This assessment should pinpoint the areas where access is being granted based on implicit trust, and help you determine which actions and endpoints need securing with additional verification layers.
Understanding the overall picture can also give you a clearer view of how security fits into your organizational culture. A successful Zero Trust Data Security implementation won’t just be an IT project; it will require participation from every division of your organization.
2. Rules and Policies
After completing an initial assessment, you’ll have a starting point for mapping out the new policies and educational initiatives needed to support your transition to Zero Trust Data Security.
Rules and policies should be devised to reflect the core principle of ZTDS: Access to sensitive data or functions can never be granted based on implicit trust. Pre-ZTDS, a user might automatically be given access based on their location (physical or virtual) or their ownership of the files in question. Your new policies should dictate that multifactor authentication or similar methods should still be used to verify the user’s identity in cases like these.
Your rules should also specify that access requests must be justified by the user’s role or work assignments and that the user should only be granted the minimum amount of privileges needed to complete their task.
Zero Trust Data Security policies should be written to protect data regardless of its location or status within the network and to apply to all access requests, whether they come directly from users or are initiated by applications via API or other software protocols. Your rules and policies should explicitly address the automated monitoring, logging, and analysis of access requests.
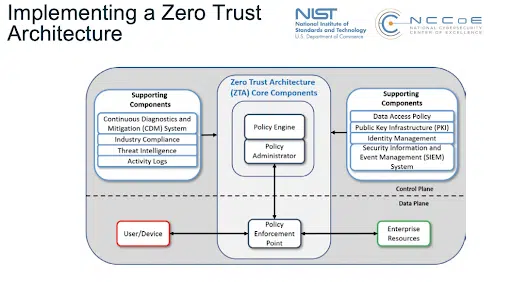
3. Training and Education
No matter how technologically secure a system is, the individuals using it will always remain points of significant vulnerability. Smarter verification methods can use contextual data like location, device, and behavior to filter out access requests from bad actors who obtained login credentials from phishing or social engineering. However, organization-wide education is essential to minimize risk and ensure optimal effectiveness of zero trust architecture.
It’s never easy giving up entrenched habits, and one of the significant challenges of Zero Trust Data Security implementation can be an organizational culture that is resistant to changing the way things have always been done. Outreach and education are often necessary to get the buy-in needed for ZTDS to be successful across the entire organization.
In addition to reducing human vulnerabilities, comprehensive employee training on how ZTDS works and why it is necessary will help your team function more proficiently within the new architecture. This will minimize delays, reduce unnecessary access requests, and prevent the mishandling of data.
Learning to Navigate the Zero Trust Environment
Don’t let misplaced trust turn your organization into the victim of a data heist. By implementing Zero Trust Data Security, you can put your cybersecurity posture on a footing fully prepared to anticipate and counter sophisticated, coordinated attacks from professional cybercriminals.
Employee education is critical because even cutting-edge defensive technologies and airtight policies can be thwarted by human error. With CybeReady’s highly engaging platform supporting your staff through the transition to the zero trust model, you can be confident that your protective measures will function as intended without slowing the pace of your workflows.
Sign up for a free demo to experience CybeReady’s innovative cybersecurity awareness training solution.












