Cyber threats are evolving with as much speed and agility as any of the tech industry’s most cutting-edge, well-funded sectors. To protect their operations and meet stakeholder expectations, businesses constantly search for better means to protect themselves from sophisticated attacks and expensive data breaches. But successful attacks are almost inevitable—and the worst consequences follow the first breach.
Once an attacker compromises a host, it takes an average of just 84 minutes before they start making incursions into other hosts within the same network. With it clear that focusing solely on preventing an initial breach is no longer sufficient, many businesses are changing their cybersecurity to the Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM).
By shifting away from an implicit trust model that automatically grants privileged access to internal users, businesses have the means to block or mitigate these lateral attacks. The average data breach cost is $4.45 million, but the ZTMM can reduce these losses by up to $1.76 million.
In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the Zero Trust Maturity Model and how it can bolster your organization’s cybersecurity.
The CISA Zero Trust Maturity Model: What is it, and why is it important?
The Zero Trust Maturity Model was developed in 2021 by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), a U.S. Department of Homeland Security division. It was designed as a roadmap for organizations to follow as they move toward a modern, zero-trust approach toward cybersecurity.
The “Zero Trust” security approach assumes that your network has already been compromised and no user or device can be fully trusted. It protects data by withholding implicit access privileges and requiring verification for any potentially risky action within the network. Instead of a location-centric model that verifies access privileges at a single point of entry, it uses identity, context, and data to make security decisions within the bounds of the network.
Organizations that operate on today’s internet offer a broad attack surface with many technological and human vulnerabilities, making it easier than ever for cyber attackers to penetrate the outer perimeter of the internal network. The Zero Trust Maturity Model ensures that bad actors who make it past the first lines of defense will not have free reign to steal or destroy sensitive data once they’re inside.
What are the 7 tenets of the Zero Trust Maturity Model?
The guide to Zero Trust architecture, published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), lays out the seven tenets of the Zero Trust Maturity Model:
- All data sources and computing services are considered resources. Anything that connects to the network, including employee-owned personal devices, can be included.
- All communication is secured regardless of network location. Internal traffic should not automatically be treated as more trustworthy than external traffic.
- Access to individual enterprise resources is granted on a per-session basis. Every request should be verified, and be granted only as much privilege as is required to complete the approved action.
- Access to resources is determined by dynamic policy—including the observable state of client identity, application/service, and the requesting asset—and may include other behavioral and environmental attributes. A variety of relevant factors should be used for setting permission-granting policies, especially where automated tasks are concerned.
- The enterprise monitors and measures the integrity and security posture of all owned and associated assets. Rather than being allowed to persist in a state of indefinite trust, assets must undergo continuous evaluation for vulnerabilities and signs of compromise.
- All resource authentication and authorization are dynamic and strictly enforced before access is allowed. Policies and technological solutions must be in place to reevaluate access privileges at appropriate intervals.
- The enterprise collects as much information as possible about the current state of assets, network infrastructure and communications and uses it to improve its security posture. Policies should be informed by insights from ongoing data analytics.
What are the stages of the Zero Trust Maturity Model?
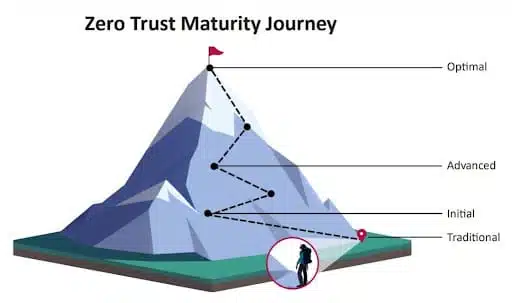
Switching a large organization over to the Zero Trust Maturity Model doesn’t happen overnight. There are four stages that an orderly transition will pass through:
1. Traditional
Fixed security policies, manual operations, and inconsistent enforcement characterize the default pre-Zero Trust state.
2. Initial
The organization begins implementing automation and increasing internal visibility, laying the foundations for ZT architecture.
3. Advanced
Centralized, automated controls are now in place for configuring asset lifecycles and assigning attributes. Policies for enforcement are becoming standardized and consistent across the entire organization.
4. Optimal
All of the tenets of the Zero Trust Maturity Model are being met with full automation, continuous monitoring, and enhanced procedures for management, enforcement, and risk mitigation.
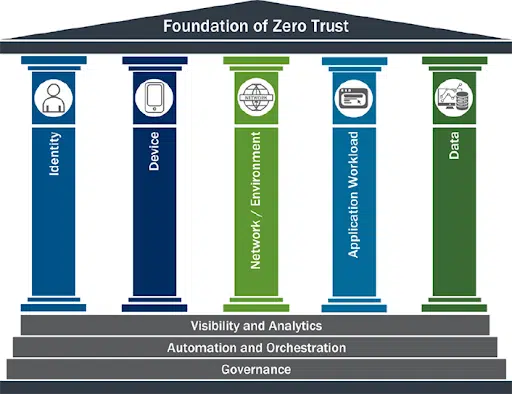
What are the 5 pillars of the Zero Trust Maturity Model?
Implementation of the Zero Trust Maturity Model takes place across five “pillars,” each with unique security requirements, which stand on a foundation consisting of three cross-cutting capabilities: visibility and analytics, automation and orchestration, and governance.
By providing this foundational support and addressing the needs of each pillar, ZTMM implementation can properly advance through the four stages.
These are the five pillars:
- Identity – Who is being granted access privileges, how are they being validated, and what does their behavior indicate?
- Devices – What hardware and software assets are connecting to the network, and how are they being inventoried and monitored?
- Networks – What are the sources of traffic flowing into, out of, and within the network?
- Applications & Workloads – How is access managed for software installations and cloud-based services?
- Data – What is being done to catalog, protect, encrypt, and monitor stored data?
What are the challenges of the Zero Trust Maturity Model?
Two of the biggest challenges to Zero Trust Maturity Model implementation are entrenched legacy systems built around an implicit trust model, and organizational cultures resistant to the operational changes that ZTMM requires.
Transitioning to Zero Trust architecture may require investments in newer technologies capable of handling granular access control, and will require buy-in at various levels of the organization. Support from the top is always critical, so it’s essential to make a strong business case for ZTMM by emphasizing its benefits, which we will outline below.
Organization-wide education about why the Zero Trust Maturity Model is needed and how to navigate systems that no longer grant access based on implicit trust will help to increase compliance, minimize friction, and speed up your progress through the stages of implementation.
What are the benefits of the Zero Trust Maturity Model?
The most significant benefit of the Zero Trust Maturity Model is that it orients an organization’s security posture toward the sophisticated, high-stakes threats that characterize the current state of cybercrime. By putting up barriers to access around the network perimeter and at every vulnerable node within it, ZTMM organizations have multiple bastions of defense against destructive cyberattacks, data breaches, and data loss.
ZTMM also gives you better visibility into your network, allowing you to isolate vulnerabilities more easily and respond faster when suspicious activity is detected.
Implementing the Zero Trust Maturity Model can confer benefits beyond cyberattack prevention. Zero Trust architecture necessitates breaking down the silos that different services often end up in, facilitating information-sharing and collaboration across all levels of the organization.
The ZTMM can also satisfy customers’ and suppliers’ demands for more robust security, and help your organization with government and industry data protection regulatory compliance.
Don’t Risk Everything You’ve Built to Misplaced Trust
Establishing a strong cybersecurity perimeter around your organization requires the right architecture. The Zero Trust Maturity Model can weave robust protection throughout your entire network and its connected assets, helping to increase your overall cyber resilience. However, technological defenses are only as strong as the people configuring and utilizing them.
CybeReady’s employee cybersecurity awareness training can ensure that everyone in your organization understands why Zero Trust matters and how to navigate it, thereby optimizing its efficacy at detecting and preventing threats.
Request a demo today to learn more about how our engaging training will educate your workforce and strengthen your company’s cyber defenses.












