Speculation about the dangers of cyber warfare has been going on since the dawn of the Information Age. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has brought full-scale cyber warfare from conjecture into reality, showing the world the clearest picture yet of what it looks like when a conflict between two nations is playing out in cyberspace. Observers on all sides are learning about the true potential of state-backed cyberattacks and how to defend against them effectively.
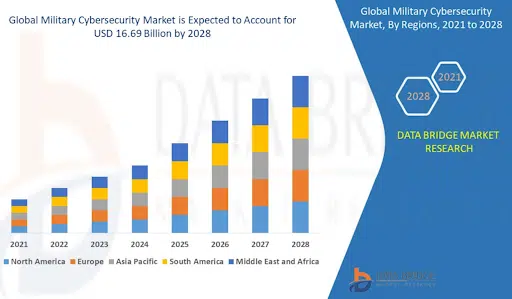
The market for military-grade cybersecurity solutions is expected to exceed $16 billion by 2028, and demand will be shaped by the successes and failures of different tactics put to the test in the war between Russia and Ukraine. Before the invasion, cybersecurity spending had already been on an upward trend in both the public and private sectors, motivated by the 440% increase in geo politically-motivated cyberattacks between 2009 and 2018.
Given the high stakes of the war and Russia’s well-established status as a backer of cyber warfare, we will learn exactly what the state-of-the-art weapons deployed to the digital battlefront are capable of. The outcome of this conflict will set the course for the cyber arms race that plays out in the years ahead, and the one thing that’s certain is that the conflict will forever change the cyber shopping market for effective security solutions.
The Cyber War in Ukraine
Russia’s cyber campaign against Ukraine started long before the February 2022 invasion. Cyber espionage, viruses, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks were deployed as early as 2013 in the run-up to Russia’s annexation of Crimea. During the annexation, Russia hacked and shut down the Ukrainian government, news, and social media sites. Many other cyberattacks have followed, including malware and ransomware attacks on industry, infrastructure, banking, and government targets.
One of the first noteworthy attacks associated with the current conflict was when Russia used data wiper malware against Viasat, an American satellite company used by the Ukrainian military, in the hours leading up to the invasion. The wiper permanently erased critical data on Viasat’s modems and routers, effectively destroying them. With Viasat down, Ukraine’s military forces were severely hindered in their ability to communicate when Russia commenced its invasion.
Russia continues to launch malware and DDoS attacks against Ukraine and its allies, particularly European countries like Poland and Germany. However, the purpose of these attacks largely appears to be harassment and demoralization without significant strategic benefits. Many cybersecurity analysts believe that the main focus of Russia’s cyber forces is digital espionage that attracts less notice—for example, hacking private security cameras to observe troop movements.
Warfare is Shifting to the Cyber Front
While the attack on Viasat was not the decisive blow Russia might have hoped for, it indicates that preemptive strikes against critical digital assets will surely be employed in future global conflicts.
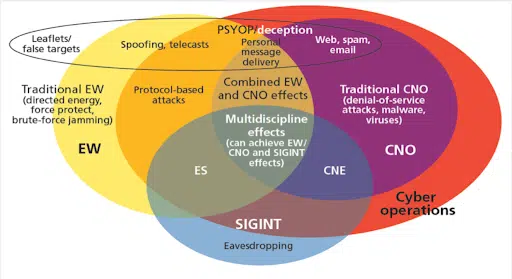
Computing and communications technology is indispensable to modern warfare, whether it’s guiding heavy munitions to precise targets through handheld devices, destabilizing civilian populations by facilitating the disruption of essential utilities and services or influencing mass sentiment through disinformation campaigns on social media. Cyberspace is now a high-priority battlefront, where supremacy has the potential to deliver major operational objectives—or at least reduce the risk and cost of achieving them.
Russia’s long history of developing sophisticated cyberattacks, and its willingness to test them on high-profile targets even in peacetime, shows that they consider the cyber front critical. Their inability to capitalize on this knowledge to bring about a swift victory in Ukraine can largely be attributed to Ukraine’s effective use of privately-developed cybersecurity solutions to defend themselves and blunt the impact of hackers, malware, and digital espionage.
How the War Accelerated Military & Private Cybersecurity Spending
Ukraine’s resilience in the face of Russia’s onslaught of cyberattacks has demonstrated the effectiveness and value of cybersecurity tools. At the same time, the volume of attacks—and the fact that they frequently strike organizations outside Ukraine—makes a compelling case that everyone is a potential target, and hardening cyber defenses is a matter of some urgency. Hostile states and activist groups are also learning from the Ukraine war, and cyber warfare will only continue to evolve in dangerous new directions.
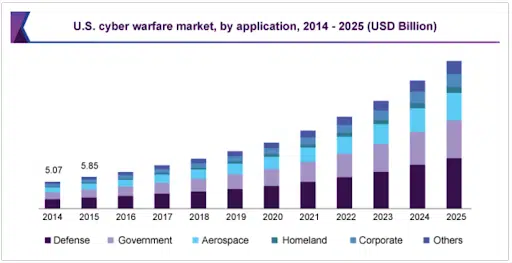
In both the public and private sectors, the Ukraine war has solidified and accelerated investments in cybersecurity. In the United States, the Federal government is proposing to spend more than $10 billion on cyber defenses in 2023. Across all organizations worldwide, cybersecurity spending is on track to hit $219 billion this year, an increase of more than 12% over 2022 spending.
The Implications for Cyberspace and Cybersecurity
Private companies have proven that they can play a central role in deflecting state-sponsored cyberattacks. Their helpfulness on this front serves to encourage further spending on private sector cybersecurity solutions that have been tested and shown to be reliable and effective. However, government and military sectors have understandable qualms about overreliance on private companies, many of them American. Some of the private sector support for Ukraine has been politically or ideologically motivated, which will not necessarily be a factor that benefits whichever parties are involved in the next global cyber war.
At the same time, a practical approach is required, particularly in the midst of an ongoing conflict. Even as public sector organizations expand their cybersecurity research budgets, they are engaging more closely with private companies and sharing information supporting more robust cyber defense capabilities.
Although many of the attacks Ukraine has fended off, have been low-grade harassment with minor strategic importance, cyber warfare that supports espionage, communications interception, and target selection can have a measurable impact on kinetic combat efforts. Improvised battlefield hardware and tactics that rely on commercial technologies like cell phones can be particularly vulnerable.
While Russia has yet to score any significant victories creditable to cyber warfare, the persistence and frequency of their efforts on the cyber front illustrate the importance of a rigorous defense. In a cyber war, defenders can’t afford to hand over an easy win by neglecting comprehensive, up-to-date security coverage.
Perhaps most significantly of all, cyber warfare knows no borders. Russia did not hesitate to attack an American company’s servers to bring down Ukraine’s communications network. Many businesses recognize that they are potential targets and are highly motivated to shop for more robust solutions to strengthen their cyber defenses.
What’s the Future of Cyber Warfare?
In a world with an ever-increasing dependence on digital infrastructure, one of the greatest threats is an attack that results in a “cyber apocalypse” that completely shuts down utilities, transportation, or communications. While this hasn’t yet happened in Ukraine, it remains a real possibility that it could occur in any conflict that escalates to a sufficient degree.
Suppose the Ukraine war provides conclusive evidence that a high volume of broadly distributed cyberattacks is insufficient to degrade enemy morale or support meaningful gains on the ground. In that case, the future of cyber warfare may involve a greater focus on innovative intelligence-gathering methods and the means to bring about a localized cyber apocalypse. Disinformation and DDoS campaigns will likely continue but may be delegated to hacktivist groups instead of the state.
In the years to come, supremacy in the cyber arms race will likely coincide with leadership in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and quantum computing. AI is already showing tremendous promise in early threat detection, and quantum computing has the potential to unravel encryption methods that are currently essential for data protection and secure battlefield communications.
How the New Context of Cyber Warfare is Affecting Cybersecurity in 2023
The high-profile hacks and breaches of the last few years, culminating in the wartime cyberattacks against Ukraine, have clarified the need for robust cybersecurity in all sectors.
Far from being the province of basement-dwelling hackers or seedy criminal groups, cyberattacks are frequently backed and funded by the full power of the states from which they originate. Instead of worrying about the ransomware that temporarily locks up their system until a payoff is made, organizations are contemplating the threat of malware that wipes out all of their data without any warning or recourse.
With these facts in mind, many organizations are rethinking their entire approach to cybersecurity. Across the globe, organizations in both the private and public sectors are investing in top-of-the-line cybersecurity solutions from vendors who have experience dealing with sophisticated attacks. Cybersecurity skills are increasingly expected of every IT professional, and company-wide training is becoming a top priority as the realization sinks in that any individual within an organization is a potential point of vulnerability.
Cyber Shopping for Arms and Security
The war between Russia and Ukraine is giving us a clear example of what a true cyber war looks like. Even though the worst consequences of cyber warfare have yet to be realized, the conflict is spurring a cyber arms race that includes not just government and military organizations, but also the private companies that can be implicated, however tangentially, in their war efforts. An unintended consequence is that a cybersecurity shopping spree has begun on a global scale, and there’s no likely end in sight.
It has always been the case that no matter how strong your technological cybersecurity measures are, they can easily be undone by human error—a fact that cybercriminals and state actors never hesitate to exploit.
The organization-wide cybersecurity training provided by CybeReady can lay the groundwork and knowledge that protects against the initial intrusions that can evade tools designed to block aggressive, high-tech threats.