“Never trust, always verify.” Sounds a little paranoid, doesn’t it? But it’s the key principle behind the security model of Zero Trust—a paradigm for our times. In a cyber world of rising threats, remote work, cloud-based services, and many other vectors with weak points that require reinforcement, it turns out that trusting no one is the safest form of cybersecurity.
However, just because you’re paranoid doesn’t mean they’re not out to get you. With hackers and ransomware gangs actively probing all sorts of systems for vulnerabilities—and attacking as soon as they find them—Zero Trust isn’t just a good idea; it’s a necessity. The cost of data breaches is reduced by around $1.76 million when Zero Trust is implemented. It’s proven effective at mitigating cybercrime, which is why 81% of cloud-based businesses are adopting it.
Jump to:
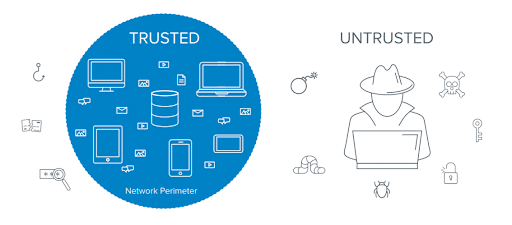
With the normalization of remote working, the vulnerability to cyber-attacks has increased, exposing a wider surface for potential threats. Conventional security measures primarily focus on defending the network’s perimeter and inherently trust users once they access internal networks. However, it has become evident that numerous organizations are falling victim to internal data breaches. Zero Trust Security directly counters this problem.
Zero Trust represents not merely a cybersecurity strategy but signifies a fundamental transformation in security perspective. It operates under a “never trust, always verify” philosophy—but what does that mean in practice?
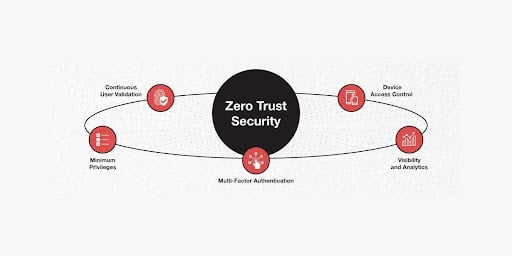
In the Zero Trust model, every user, device, and application, regardless of their position relative to the network boundary, undergoes stringent authentication, authorization, and ongoing verification before gaining access to resources. It recognizes that threats can originate from outside and inside the network, necessitating a universally applicable set of guiding principles and architectures.
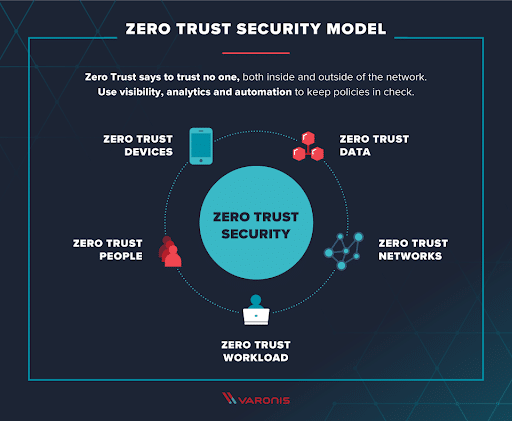
The essential elements of Zero Trust include:
Zero Trust is globally recognized and the approach favored by top tech companies to enhance cybersecurity. Adopting Zero Trust Security offers numerous advantages:
The architecture of Zero Trust security is underpinned by seven fundamental pillars:
This pillar utilizes essential security mechanisms like access control policies and authentication to verify users before granting network access, effectively reducing possible attack surfaces.
This ensures the identification and authorization of devices, ranging from user-controlled to autonomous IoT devices, seeking connection to organizational resources.
This pillar involves securing applications, digital processes, and IT resources against unauthorized access, breaches, and tampering by reinforcing each workload with protective measures.
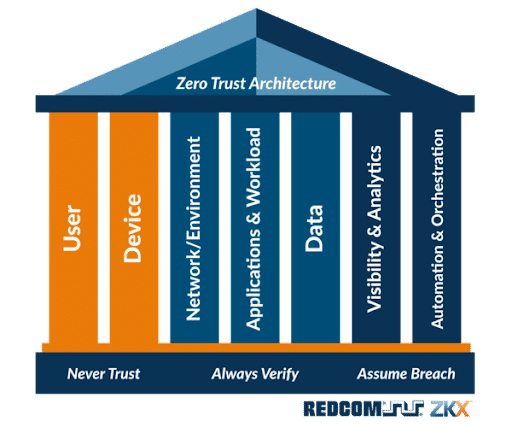
Within Zero Trust, this pillar is crucial for implementing micro-segmentation and isolating sensitive resources to bar unauthorized access.
This pillar entails meticulous data categorization and restriction to authorized personnel, alongside determining secure data storage locations and implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit.
Comprehensive monitoring, possibly leveraging AI, is essential for overseeing access control, segmentation, encryption, and data organization, and for automating anomaly detection and configuration control.
This addresses the streamlined automation and centralized management of the Zero Trust model across diverse networks and data centers.
Each of these pillars plays a significant role in fortifying the security posture of organizations by systematically reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing protective measures.
The Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM) was introduced in 2021 by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), an arm of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. This model serves as a guide for enterprises transitioning to the contemporary Zero Trust method for cybersecurity.
The Zero Trust strategy operates on the premise that a breach has already occurred within your network, meaning no user or device is inherently trusted. Rather than granting automatic access rights, it mandates validations for any action that could pose a threat inside the network. Unlike traditional models that anchor access permissions to a singular entry point, this approach determines security permissions based on identity, context, and data within the network’s confines.
Given the vast array of tech and human weak points in modern online operations, organizations present an expansive target for cyber threats. This makes it relatively simple for cyber adversaries to breach the initial protective barriers of internal networks. By implementing the Zero Trust Maturity Model, organizations can ensure that even if intruders penetrate the primary defenses, they won’t have unrestricted access to critical data internally.
One of the main obstacles to adopting the Zero Trust Maturity Model is deep-rooted legacy systems that operate on an inherent trust framework. Additionally, organizations often grapple with internal cultures that are hesitant towards the procedural shifts demanded by ZTMM.
Shifting to the Zero Trust framework might necessitate financial commitments in advanced technologies adept at detailed access management. Moreover, it’s pivotal to garner support from different organizational tiers. Getting an endorsement from senior leadership is critical, so spotlighting the advantages of ZTMM through a compelling business rationale is often needed to get buy-in.
Educating the entire organization on the importance of the Zero Trust Maturity Model and guiding them through systems that no longer operate on assumed trust can bolster adherence, reduce hurdles, and expedite the transition phases.
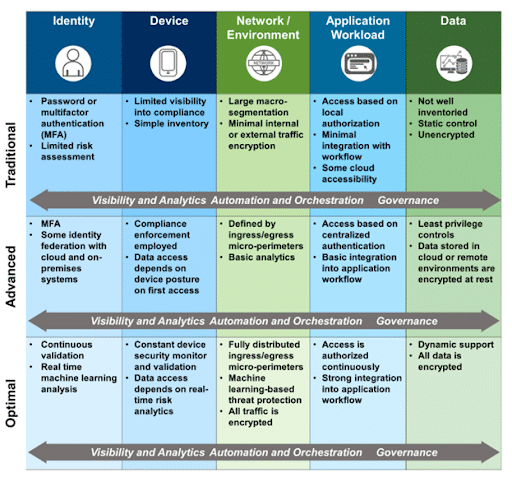
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released a guide on Zero Trust architecture, outlining the seven fundamental tenets of the Zero Trust Maturity Model:
Transitioning a substantial organization to embrace the Zero Trust Maturity Model is a four-phased process.
It begins with the ‘Traditional’ phase, where security measures are set, operations are manually conducted, and the enforcement of policies is sporadic. As the transition commences, the ‘Initial’ phase sees the onset of automation and heightened internal transparency, setting the stage for the Zero Trust architecture.
Progressing further, the ‘Advanced’ phase introduces centralized, automated controls for managing assets and standardizing enforcement policies throughout the enterprise. Finally, in the ‘Optimal’ stage, every Zero Trust Maturity Model principle is fully realized with top-tier automation, relentless monitoring, and improved management and risk-reduction strategies.
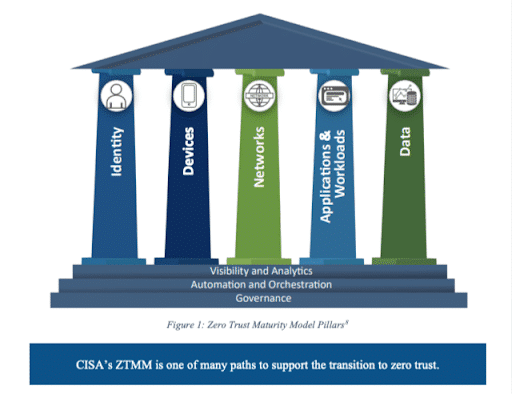
The Zero Trust Maturity Model is structured around five core “pillars,” each encompassing distinct security aspects. These pillars are grounded on a trio of foundational capabilities: visibility and analytics, automation and orchestration, and governance.
Ensuring that this foundational trio supports and caters to the unique requirements of each pillar allows the Zero Trust Maturity Model to evolve through its four progressive stages.
Here’s a breakdown of the five pillars:
The primary advantage of the Zero Trust Maturity Model is its alignment with an organization’s security measures to counteract the intricate and high-risk threats prevalent in today’s cybercrime landscape. By establishing protective measures at the network’s edge and at every potential weak point inside, organizations employing ZTMM provide multi-layered defenses against harmful cyberattacks, data breaches, and information losses.
ZTMM also enhances an organization’s insight into its network, enabling quicker identification of weak spots and rapid response to unusual activities.
However, the benefits of adopting the Zero Trust Maturity Model extend beyond merely thwarting cyber threats. The Zero Trust framework promotes the dissolution of isolated service compartments, fostering improved information exchange and collaboration throughout the organization.
Organizations can meet the rising security expectations of clients and suppliers by adopting ZTMM, and better align with regulatory standards set by governments and industries for data protection.
Focusing solely on fortifying the network’s outer boundary and inherently trusting any user who gains entry creates a potential risk. With just one vulnerable point or compromised account, every piece of data, device, and application could be jeopardized.
The essence of Zero Trust Data Security (ZTDS), also known as Zero Trust Data Protection, lies in the belief that trust necessitates verification. The fundamental presumption should be that the system is already compromised, and protective measures should aim to minimize the fallout.
Every data access or modification attempt must undergo thorough scrutiny, taking into account comprehensive user details like their identity, gadget, location, and past behavior.
When permissions are assigned, they should strictly follow the principle of minimal privilege. Users should only have access aligned with their designated role or specific task, confined to the necessary time period, without any superfluous permissions (for instance, someone who just requires reading access shouldn’t be able to alter or remove records). Monitoring user activities and implementing rules should be as automated as feasible.
Zero Trust Data Security bolsters your defenses against cybercriminals, ensuring that even if they breach your network, causing widespread harm becomes challenging. Here’s how it augments your protection and offers added advantages:
Zero Trust Data Security is implemented through a progressive, three-fold approach.
First, the principle of data resiliency ensures that every piece of data is encrypted and securely backed up, laying the groundwork for enhanced protection and efficient recovery.
Following this, data access is managed using role-based access controls combined with multi-factor authentication. This ensures that only authorized individuals can view or alter the data.
The final phase involves the persistent surveillance of the network. Advanced technologies, including machine learning and predictive artificial intelligence, play a pivotal role in detecting early signs of data breaches.
Transitioning an organization to a Zero Trust Data Security model is intricate. This transition revolves around three critical steps: assessment, policy formulation, and training.
During the assessment phase, it’s imperative to examine the present data protection protocols. This involves understanding the nature and locations of stored data, determining who requires access and why, comprehending the software involved, and grasping how data moves within the network.
Equally important is recognizing potential risk factors. A comprehensive assessment reveals the gaps in the current system, especially where access is given without stringent verification. For ZTDS to permeate an organization effectively, every department must be involved, ensuring that security isn’t just confined to the IT division.
Post-assessment, the focus shifts to formulating rules and policies. The essence of ZTDS is that access shouldn’t be granted merely based on assumptions or implicit trust. The same stringent rules must apply whether the data request is from users directly or through applications. This means that even if a user seemingly has the right to access data, multi-factor authentication or other verification methods should be in place.
Access should always be minimal, based solely on the user’s role or specific assignments. Another pivotal aspect is ensuring the policies are robust enough to protect data irrespective of where it resides within the network.
Lastly, training and education play a paramount role. No matter how secure, a system is only as strong as its users. While sophisticated verification techniques can help deter unauthorized access, the human element often remains susceptible. Introducing a change as monumental as ZTDS is challenging, especially if it diverges from long-standing practices. Organizational culture might resist such shifts.
An extensive training program emphasizing the significance and workings of ZTDS is essential. Well-informed employees can operate seamlessly within this new framework, mitigating risks and ensuring the smooth flow of operations.
Fortifying your organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure is critical, and the Zero Trust Maturity Model provides a comprehensive approach used by leading tech firms. This model encapsulates the belief that no entity, internal or external, should be blindly trusted, and every access request has to be authenticated and authorized. While technology forms the backbone of this robust security paradigm, the human element is just as crucial.
The foundation of any successful Zero Trust initiative lies in the hands of the workforce. Employees are often on the front lines when it comes to identifying cyber threats, so their training and awareness are vital. CybeReady offers top-tier cybersecurity awareness training programs, uniquely designed to help employees swiftly recognize and respond to potential threats.
By integrating state-of-the-art tools like phishing simulations and tailored training modules, CybeReady ensures that your team is well-equipped and develops a culture of security awareness—transforming them into the most formidable defense against escalating cyber risks.
If you’re ready to harness the combined might of Zero Trust security and a well-trained, cybersecurity-aware workforce, contact CybeReady to learn how.





Copyright © 2025 – CybeReady
We will reach out to you shortly.
In the meantime, please check out our complimentary CISO Tool Kit
Wir werden uns in Kürze bei Ihnen melden.
Schauen Sie sich bitte in der Zwischenzeit das kostenlose CybeReady CISO Tool Kit an.
We will reach out to you shortly.
In the meantime, please check out our complimentary CISO Tool Kit, or visit Our Blog
We will reach out to you shortly.
In the meantime, please check out our complimentary CISO Tool Kit, or visit Our Blog