What do cybercriminals want? Your money. When do they want it? All the time. And how do they get access to it? By exploiting the combination of digital banking and our trust in financial services and institutions. Among the tools and tactics cybercrooks frequently use to pull off their heists are trojans. One notable example is the Tiny Banker (Tinba) trojan that infected the computers of more than 20 major US banking institutions.
Trojans are an evolving threat, with global financial losses estimated in the millions. A recent study discovered 200,000 new mobile banking Trojans in 2022 alone. Since Tinba’s peak in 2016, this banking trojan has been considered one of the most destructive malware strains plaguing the banking industry and is still employed in various forms. Let’s get to know it a little better.
What is Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba), and how does it work?
Tinba (a shortened version of the name Tiny Banker) is a malware specifically designed to target financial institutions and their customers. A smaller version of Zeus Trojan, Tinba (also referred to as Zusy), was initially discovered in 2012. Its source code was leaked onto the Internet in 2014, leading to further evolution and variants of the malware.
Primarily targeting systems running on Windows, Tinba typically infiltrates through phishing emails, compromised websites, or malicious downloads disguised as legitimate links, attachments, or ads. Once it infiltrates a user’s computer, it stealthily operates in the background, slipping past security programs to capture sensitive information such as keystrokes and mouse movements during online banking activities.

When installed, Tinba uses a variety of techniques to steal sensitive information, including:
- Packet Sniffing – This technique allows Tinba to intercept data packets between your device and the bank’s website, revealing your login credentials and other critical information.
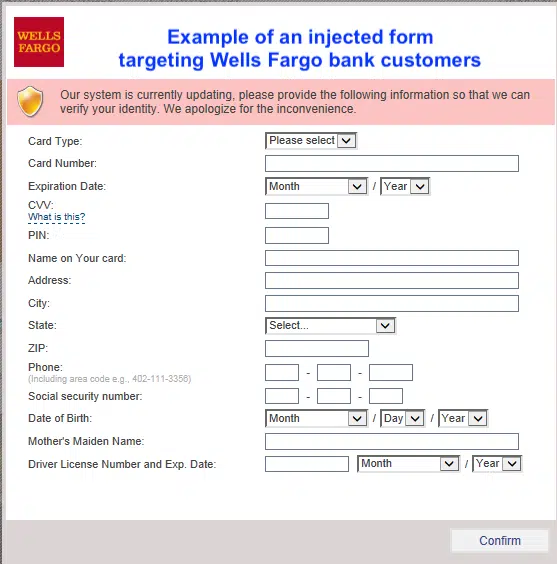
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks – Tinba can inject itself into the communication channel (such as your browser) between your device and the bank, intercepting and manipulating data in real time. This can result in fake prompts appearing on your screen, requesting sensitive information like passwords or credit card details.
- Keylogging – Tinba can record every keystroke you type, capturing your login credentials and other sensitive data.
- JavaScript Injection – Tinba has a web injection feature that includes harmful JavaScript code. This component of the malware is capable of performing dynamic web injections on various online banking platforms. It precisely mimics the appearance of the original banking sites, making it challenging for users to detect discrepancies.
The information Tinba gathers is transmitted to a control site managed by cybercriminals, where your stolen credentials are used to access bank accounts, transfer funds, and make fraudulent purchases.
Due to its compact size (20 KB) and ever-adapting methods, Tinba presents a significant challenge for conventional antivirus programs to detect and eradicate effectively, positioning it as a consistent and formidable threat in the cybercrime landscape.
Why should you care about the Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba)?
The consequences of a Tinba infection can be devastating. Individuals can suffer financial losses, including unauthorized withdrawals, credit card fraud, and identity theft.
Financial institutions can face costly data breaches, reputational damage, and operational disruption. Legal and compliance consequences may result in regulatory fines and compensation of affected parties. A Tinba attack also adds additional expenses for removing the malware, along with comprehensive cybersecurity reassessment and upgrades.

(Source: Banking Trojans: From Stone Age to Space Era)
It’s worth noting that Tinba will no longer be as widespread in 2024, with up-to-date anti-malware solutions more than capable of detecting and stopping it. However, Tinba / Zusy has since evolved due to its open-source nature, with Tinba v2 detected in the wild by IBM security researchers.
Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba): Detection and Remediation
Detecting Tinba: Early Warning Signs
Early detection is critical to containing a Tinba infection and minimizing its impact. Here are some red flags that might indicate Tinba activity:
- Unusual network activity – Increased network traffic, particularly to unknown IP addresses, can indicate malicious communication.
- Suspicious website behavior – Unexpected redirects, pop-up messages, or website appearance changes can indicate a compromised website or MITM attack.
- System performance issues – Slowdowns, crashes, or unusual resource consumption can indicate malware activity.
- Account anomalies – Discrepancies in account balances, unauthorized transactions, or login attempts from unrecognized locations should be investigated.
- Employee reports – Employees reporting suspicious emails, phishing attempts, or website anomalies are valuable early warnings.
Remediating Tinba: Swift Action is Crucial
Once a Tinba infection is detected, immediate action is required to contain the damage and prevent further spread. Here’s a recommended course of action:
- Disconnect compromised devices from the network immediately to prevent lateral movement of the malware.
- Conduct a thorough forensic investigation to identify the extent of the infection and isolate infected devices.
- Run comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware scans to remove Tinba and other malicious software.
- Change all compromised passwords, security questions, and other credentials for affected accounts.
- Analyze how the infection occurred to identify and address vulnerabilities in your security posture.
- Update software and operating systems to ensure all known vulnerabilities exploited by Tinba are patched.
- Inform stakeholders about the incident and provide relevant security awareness training to employees.
Get Proactive: 5 Components of an Effectively Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba) Mitigation Strategy
Tinba’s sophisticated nature demands a multi-layered approach to defense, with a combination of technological tools and preparation of the human element. Since human error or oversight is the leading cause of trojan infections and data breaches overall, it’s vital that you focus on building your human firewall and complement it with technological solutions for automation and enforcement of security best practices.
1. Prioritize user education
As we all know, knowing is half the battle. Being aware of the Tiny Banker trojan and its potential consequences is key to preventing infection. CybeReady offers security awareness training that equips employees with the skills and knowledge to identify and avoid phishing attempts – the most common vector in spreading Tinba. In addition to recognizing and avoiding Tinba in phishing emails, you should ensure your employees are guided to:
- Use and update the endpoint security solutions on their devices. Current anti-malware tools can detect and effectively block Tiny Banker and other trojans.
- Be vigilant and pay attention when entering sensitive information in banking apps or websites. They should be especially suspicious when the bank suddenly asks for information they typically do not or when they notice suspicious flaws or changes to the website design or URL.
- Install applications from trusted sources only, especially when it comes to banking apps. Double-check the application’s source, even if you find it on Google Play or the Apple App Store.
- Maintain strong password hygiene by using complex passwords and never reusing passwords across services.
2. Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a powerful deterrent against unauthorized access attempts. Requiring additional factors like biometrics or security tokens for account access significantly improves security beyond SMS verification, which is vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks. A robust identity management policy is recommended for optimal security.
3. Manage Software Vulnerabilities
Tinba often exploits outdated software vulnerabilities to gain access to systems. Regularly update software and operating systems so that vulnerabilities are patched promptly, minimizing the risk of infection. Implementing a centralized patch management system automates the process of deploying updates across your organization’s devices. Prioritize patching critical vulnerabilities identified by security researchers and software vendors.
4. Implement Advanced Endpoint Security Solutions
Deploying advanced endpoint security solutions provides real-time protection against malware threats. These solutions employ techniques like signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and sandboxing to identify and neutralize malicious code.
Regularly updating virus definitions and threat intelligence databases ensures these solutions remain effective against the latest malware strains. Implementing endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions further strengthens endpoint security by providing advanced threat detection and investigation capabilities.

5. Proactively Monitor and Analyze
Continuous network monitoring and activity analysis of security logs are crucial for detecting early signs of Tinba activity. The use of the following tools is recommended:
- Network security monitoring tools help identify unusual network traffic patterns associated with malicious activity.
- Web application firewalls (WAFs) filter malicious traffic and protect web applications from vulnerabilities exploited by Tinba.
- Leveraging SIEM (security information and event management) systems allows for comprehensive log analysis, identifying potential security threats and anomalies before they escalate into major breaches.
- Website spoofing prevention solutions monitor, alert, and protect against duplicate, fraudulent websites that inject malware and steal financial data.
The monitoring and analysis of your systems must be combined with a similar approach to evaluating employee readiness and defensive cybersecurity skills. Make periodic assessments of company-wide cyber-readiness and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Security Awareness Is the First Line of Defense
The Tiny Banker Trojan (Tinba) continues to pose a threat to financial organizations and their customers, causing economic losses and reputational damage. By implementing these practical steps and fostering a cybersecurity awareness culture in your organization, you can significantly reduce the risk of Tinba infections and protect your sensitive financial data from falling into the wrong hands.
Employees educated on the latest cyber threats and how to detect them create a Human Firewall of security awareness—the first line of defense against banking Trojans like Tinba. CybeReady’s programs are engaging, offered in forty-two languages, and deploy 8x more phishing simulations and ongoing cybersecurity awareness bites without any extra effort from IT. Try a free demo of CybeReady today.