The consequences of cyberattacks are damaging to businesses and individuals and have far-reaching implications for society as a whole. Global cybercrime costs are projected to grow at an alarming rate of 15% per year over the next five years, with an estimated annual cost of $10.5 trillion by 2024. These staggering figures underscore the urgent need for proactive approaches and robust cybersecurity measures.
To address these pressing concerns, the European Commission has proposed the Cyber Resilience Act 2023 (CRA) as a pivotal step toward fortifying cybersecurity and enhancing cyber resilience within the European Union (EU). With its focus on implementing mandatory cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements, the CRA aims to create a more secure digital landscape.
In this guide, we’ll look at the importance of the Cyber Resilience Act, its benefits and challenges, and its potential impact.
What is the Cyber Resilience Act, and how does it work?
The Cyber Resilience Act 2023 is a proposed regulation to improve cybersecurity and cyber resilience within the EU. It targets manufacturers and retailers of products with digital elements, such as hardware, software, and IoT devices. The CRA introduces mandatory cybersecurity requirements throughout the product lifecycle, from design and development to use and disposal.
The CRA addresses the growing number and sophistication of cyberattacks by implementing cybersecurity by design and default principles, conducting cybersecurity risk assessments, ensuring security updates and patches, reporting cybersecurity incidents, and providing users with product cybersecurity information.
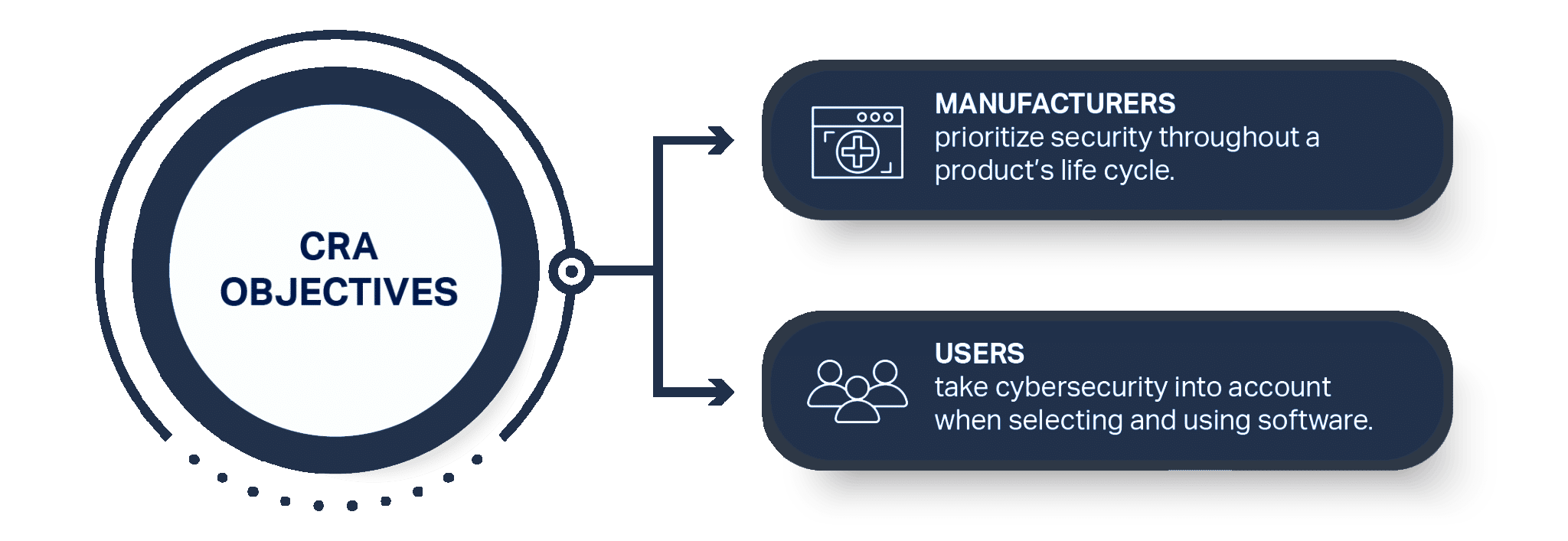
The draft CRA would require manufacturers to conduct a cybersecurity risk assessment and build hardware and software with an appropriate level of cybersecurity. It also includes provisions such as monitoring and recording device activity, vulnerability disclosure policies, and providing free security updates. The regulation covers a wide range of hardware and software, applying the same cybersecurity requirements but adapting the conformity assessment based on the risk level.
ENISA, the EU cybersecurity agency, would play a central role in implementing the CRA. Market surveillance authorities of EU member states would enforce the regulation, with the ability to impose penalties for non-compliance. The European Commission would intervene in exceptional circumstances to ensure compliance and can restrict or temporarily remove non-compliant products from the EU market.
The CRA, once adopted, will contribute significantly to improving cybersecurity and cyber resilience in the EU. It will enhance digital defenses, increase consumer and business cybersecurity, reduce the risk of cyberattacks, and create an improved market for cybersecurity products and services. As organizations navigate the evolving cyber threat landscape, the CRA will play a crucial role in strengthening digital defenses and ensuring a more secure digital future.
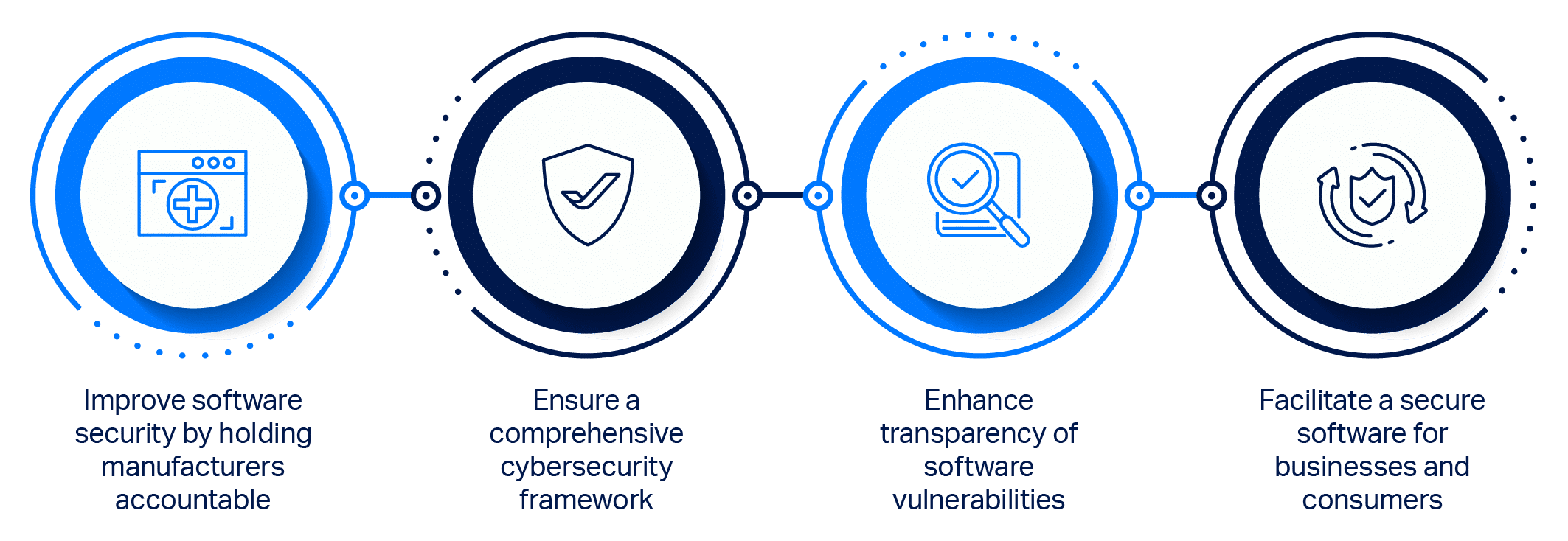
What are the benefits of the CRA?
The CRA brings several significant benefits to consumers and businesses in the EU:
Enhanced Cybersecurity
The CRA enforces mandatory cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements, leading to improved security measures. These reduce the risk of cyberattacks and safeguard digital products from potential vulnerabilities.
Increased Consumer Confidence & Trust
Consumers can feel confident that the physical and digital products in the EU market will offer enhanced security, protecting their data and privacy while enhancing trust.
Improved Market Conditions
Mandatory cybersecurity requirements create a more favorable market for cybersecurity products and services. The CRA encourages innovation and competition in the industry, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Reduced Cyberattack Risks
The CRA’s focus on cybersecurity risk assessment and security by design helps organizations identify and address potential vulnerabilities. The likelihood of successful cyberattacks is significantly reduced by proactively mitigating risks.
Strengthened Digital Defense
Some of the proposal’s obligations—such as monitoring internal activity, implementing security updates, and limiting attack surfaces—contribute to strengthening an organization’s digital defense and resilience.
Compliance with EU Regulations
The proposal helps ensure compliance with EU regulations by introducing cybersecurity requirements for manufacturers and retailers, which supports the EU’s efforts to create a more secure digital ecosystem.
Certification and CE Marking
The CRA establishes an EU cybersecurity certification scheme. Manufacturers can obtain certification to demonstrate compliance with the required cybersecurity standards. Certified products will carry the CE marking, serving as a visible indication of their adherence to cybersecurity requirements.
What are the challenges of the CRA?
The CRA is a comprehensive and intricate piece of legislation—requiring careful consideration of technical requirements, industry-specific needs, and compliance processes.
Striking a balance between stringent cybersecurity requirements and practical implementation for manufacturers and retailers will be challenging. Simply meeting the obligations of conducting cybersecurity risk assessments, implementing security by design and by default principles, and providing free security updates will require careful monitoring, planning, and resource allocation.
On top of that, the CRA applies to a wide range of hardware and software with digital elements, which puts the onus on manufacturers in different sectors to ensure that the requirements can be effectively met across various product categories and technologies.
The proposal also introduces obligations for manufacturers to monitor and record device activity, keep records of vulnerabilities, and report security breaches to the EU cybersecurity agency (ENISA). Establishing the necessary processes and systems to meet these requirements may involve administrative burdens.
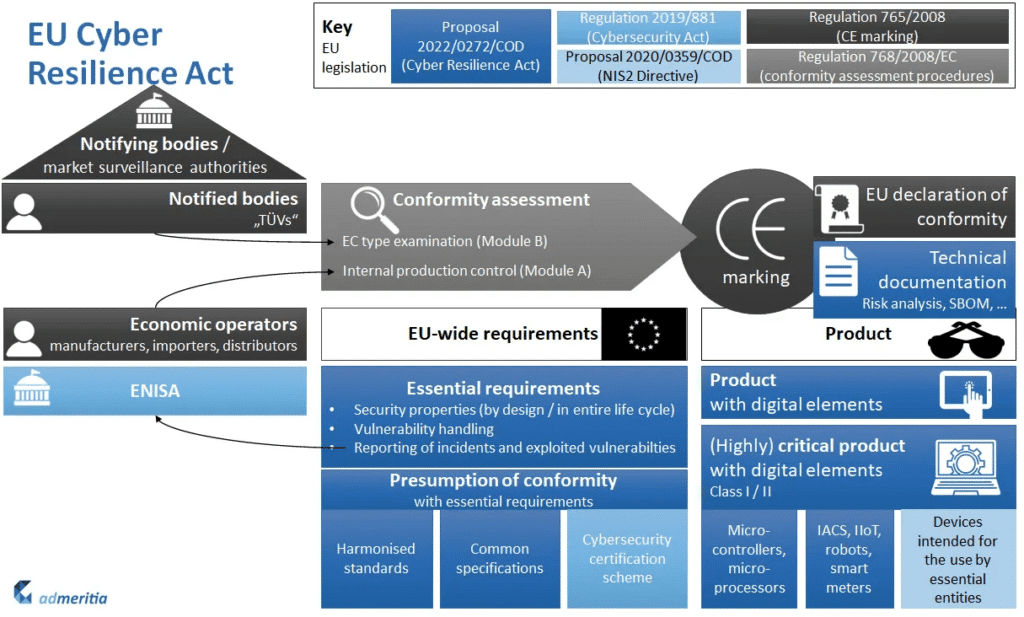
These burdens will be spread throughout the Market Surveillance Authorities (MSAs) of EU member states that are responsible for enforcing the CRA and imposing penalties for non-compliance. Ensuring consistent enforcement and coordination among MSAs is crucial for effectively implementing the legislation.
Despite these challenges, it is essential to address them proactively to realize the full potential of the CRA and bolster cyber resilience across the EU. Fostering collaboration and awareness among manufacturers, retailers, regulatory bodies, and cybersecurity experts is vital to overcoming these obstacles and ensuring a smooth implementation process.
5 Ways the CRA Strengthens Your Digital Defenses
1. Cybersecurity by Design and Default
Manufacturers are obligated to implement cybersecurity by design and default principles. Security measures must be embedded into the products from the very beginning, reducing vulnerabilities and fortifying their resilience against cyberattacks.
2. Cybersecurity Risk Assessment
The CRA mandates that manufacturers conduct cybersecurity risk assessments for their products. This proactive approach allows organizations to identify potential threats, assess their severity, and take appropriate preventive actions to mitigate risks.
3. Security Updates and Patches
The CRA emphasizes the importance of regular security updates and patches. Manufacturers must ensure their products receive timely updates to address emerging vulnerabilities and counter new attack vectors.
4. Mandatory Reporting of Cybersecurity Incidents
The CRA requires manufacturers to report any cybersecurity incidents to ENISA promptly. This reporting mechanism promotes transparency, facilitates quick incident response, and enables effective remediation measures.
5. User Information and Awareness
Another vital aspect of the CRA is the provision of information to users about the cybersecurity of products. By ensuring users are well-informed, they can make educated decisions and take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their digital assets.
The CRA: Embracing the Future of Cyber Resilience
The CRA represents a significant step forward in improving cybersecurity and cyber resilience in the EU. By embracing this regulatory framework, organizations can enhance their digital defenses and ensure the safety of their operations, reputation, and customer trust.
However, building a culture of cybersecurity awareness remains the first line of defense in this ever-evolving landscape. As a leader in cybersecurity training, CybeReady offers comprehensive programs that create a resilient workforce capable of effectively identifying and mitigating cyber threats.
Take action today by requesting a demo to experience CybeReady’s employee awareness training solutions. Let’s fortify our digital defenses and pave the way for a secure, resilient future.