Often, vulnerability management gets compared to a game of whack-a-mole, where you deal with one vulnerability and two more pop up. This hints that vulnerability management is not an event; it’s a process. But this process doesn’t have to come with the frustration of constantly putting out fires.
A vulnerability is a weakness in a system’s code, controls, processes, or configurations that a threat actor can exploit to conduct a cyber attack. With recent research finding more than800 dangerous vulnerabilities in the average company’s IT environment, it’s clear that vulnerability management isn’t where it needs to be.
This article explains how vulnerability lifecycle management enables you to handle vulnerabilities and reduce your cybersecurity risk exposure from weaknesses in your environment. You’ll also get five actionable best practices to improve vulnerability management in general.
What is vulnerability lifecycle management?
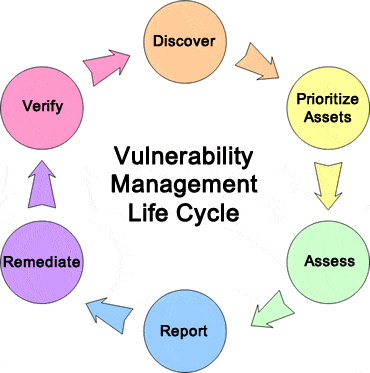
Vulnerability lifecycle management takes a cyclical approach to identifying, prioritizing, and remediating security weaknesses. Illustrating the process in this way reinforces the idea of vulnerability management as continuous rather than something you do at a certain time each year and then forget about.
Vulnerability management vs. vulnerability assessment
The main difference between vulnerability management and assessment is that the former is an ongoing process while the latter has a defined start and end date. A vulnerability assessment provides a snapshot of the vulnerabilities within a system or environment. Vulnerability management is an overarching, continuous strategy for identifying, managing, and mitigating vulnerabilities. Conducting vulnerability assessments plays a vital role in vulnerability management, but it’s just one part of a much broader approach.
5 ways vulnerability lifecycle management can keep you out of trouble
1. Identify security weaknesses
With expanding attack surfaces, hybrid working arrangements, and cloud computing, IT ecosystems are more complex than ever. It’s no longer straightforward to know where to look for vulnerabilities. A simple glance at a few on-premise apps and lists of company hardware/software won’t suffice.
Potential weaknesses lurk in many places, from vulnerable without the knowledge or approval of your IT department. By requiring a formal discovery process that creates an asset inventory of all known and shadow IT assets, vulnerability management gives you a much better chance of identifying all the security weaknesses that threaten your cyber defenses.
2. Prioritization of assets
Another benefit of the lifecycle approach is that it doesn’t just lump all assets into a single category and then try to find weaknesses. Such an approach is a recipe for wasted time and effort on weaknesses that don’t really pose a risk. The broad-stroke method can inundate people with too much vulnerable data to sift through, leading to frustration and stress.
Vulnerability lifecycle management gets to the crux of your riskiest security weaknesses by identifying the most critical assets for your company’s ongoing operations, especially those that contain sensitive data or pose business continuity threats if attacked. This prioritization also accounts for the threat exposure of assets so that systems that aren’t reachable without physical access are perceived as less likely to be breached, even if they contain exploitable vulnerabilities.
3. Assess, report, and remediate the weaknesses
The structured approach of vulnerability lifecycle management then proceeds through traditional vulnerability assessments that create helpful reports that outline all discovered vulnerabilities and their risk/prioritization level. This report then makes it much easier to apply appropriate remediation measures based oncyber risk rather than a scattergun approach to remediation.
4. Verify the weaknesses have been eliminated
Since new vulnerabilities continually emerge over time, it’s often tempting to just apply patches or other fixes to the vulnerabilities you’ve already found and then forget about them. But it’s important to double-check that any remediation has the desired effect.
Vulnerability lifecycle management has a reassessment stage that verifies the success or failure of any actions taken to remediate vulnerabilities. Sometimes you might find that more than merely limiting the exposure of an asset is needed and that a complete security patch is needed.
5. Continuous improvement
The cyclical approach provides a good opportunity to foster continuous improvements to vulnerability management and your overall security program. With each new cycle, leverage data and feedback from previous reports and assessments to figure out better ways of doing things, whether that means updating your security policy or using a more advanced vulnerability scanner.
5 vulnerability management best practices
1. Follow a framework
With anything complicated, having a framework to assist you is always helpful. A framework provides a basic structure or foundation to follow when carrying out a process. For vulnerability management, consider NIST’s Guide to Enterprise Patch Management Planning. For a framework applicable to the entire process (not just patch management), consider the elements of NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework.
2. Scan all devices regularly
Industry recommendations indicate scanning for vulnerabilities at least quarterly. The more regularly you scan your devices, the better your chances are of catching vulnerabilities before they get exploited by malicious actors. While you might feel that a daily scan is excessive, quarterly might not be frequent enough; a good balance is to aim for a monthly scan of all devices.
3. Provide training in secure practices
Many cybersecurity vulnerabilities emerge due to human error, and these errors are more likely to occur if your employees lack effective cybersecurity training and awareness. From leaving sensitive data available in publicly accessible storage systems to using out-of-date and vulnerable open-source components in apps, these possibilities must be reduced if you want to improve vulnerability management.
If the burden of training is too resource-intensive, look for solutions or platformsthat automate much of the process by delivering personalized training materials to users. Focus less on lengthy and generic materials and more on bite-sized training that’s constantly reinforced.
4. Implement automation
Vulnerability management is an area that calls for as much automation as possible. Managing potentially thousands of vulnerabilities is daunting; therefore, businesses often end up in an unacceptable situation where it takes 256 days to patch severe vulnerabilities. Generally, repetitive and menial tasks are good candidates for automation. Candidates for automation include automating your asset inventory, automated remediation workflows, and automated patch management.
5. Define, measure, and review program metrics
Improvements to your vulnerability management program don’t arise just because you repeat the process regularly. What’s important is to define and measure useful metrics that guide the changes you can make or the weak areas of your approach.
Some important metrics to measure and review include:
- Mean time to remediation.
- Rate of vulnerability recurrence.
- The number of critical vulnerabilities (e.g., CWE Top 25).
- Scanning coverage.
Cybersecurity awareness training can help you manage your vulnerabilities effectively
Vulnerability lifecycle management can help you identify more vulnerabilities, use a more efficient risk-based approach to vulnerability management, and provide a structure for continually improving how you handle vulnerabilities. Combined with applying best practices, these strategies can supercharge vulnerability management.
But it’s important not to overlook the human side of vulnerability exposure. Weaknesses in your code, systems, and infrastructure are less likely to emerge or be exploited when you have a cyber-aware workforce. Traditional cyber awareness training is often ineffective because it relies upon impersonal and lengthy training materials provided to employees on an ad hoc or irregular schedule.
CybeReady changes the game with a platform that automatically delivers employees consistent, personalized, bite-sized cybersecurity awareness training. Materials are fun and engaging, making lessons easier to remember and mistakes less likely to occur.